Application of Donabedian Three-Dimensional Model in Outpatient Care Quality: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 40313787
- PMCID: PMC12045680
- DOI: 10.1155/jonm/6893336
Application of Donabedian Three-Dimensional Model in Outpatient Care Quality: A Scoping Review
Abstract
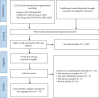
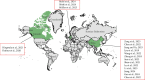
Background: The mobility of outpatients, frequent treatment sessions, and varying illness severity challenge nursing care and hinder quality improvement efforts. The Donabedian model effectively evaluates nursing quality and is widely used in operating rooms, intensive care units and oncology wards. However, its application in outpatient nursing remains unclear. Aim: To overview the Donabedian model's application in outpatient care quality. Methods: A scoping review was conducted using the Arksey and O'Malley framework, adhering to PRISMA-ScR. Searches for eligible papers were performed on PubMed, OVID, Web of Science, Embase, CNKI, CBM, and Wan Fang in June 2024. Data were analyzed narratively using an inductive approach, with visual mapping done through ArcGIS and Origin. Results: A total of 18 studies were included in the review. Literature review, Delphi and semistructured interview were widely used in the mixed method studies. The primary settings involved dental clinics and health examination centers, followed by traditional Chinese medicine clinics and pediatric clinics. The studies spanned various regions: 2 in Canada, 3 in Germany, and 13 in China. Structural indicators evaluate outpatient care systems and resources, while process indicators emphasize specialty nursing practice, safety, infection control, and humanistic care. Satisfaction, adverse events, and quality care serve as key secondary indicators for outcome assessment. Conclusions: The research on outpatient care quality based on the Donabedian model is primarily mixed, with a need to expand interventional and qualitative studies. The structure-process-outcome quality indicators have varying focuses that require further verification and coordination. Structural indicators offer more policy and resource support, while process indicators differ across outpatient specialties, leading to heterogeneous specialist nursing practice metrics. Satisfaction and adverse events are crucial components in evaluating outpatient nursing quality outcomes. Implications for Nursing Management: The application of the Donabedian model offers care managers practical ideas and references for outpatient care quality improvement.
Copyright © 2025 Jinrong Yang et al. Journal of Nursing Management published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen L., Xi X. The Study of Evaluation for the Quality of Extended Care Based on Donabedian Model of Care. Chinese Nursing Management- . 2015;15(06):713–717. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2015.06.023. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources