Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Atherogenic Index as Alternative Biomarkers for Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 40314056
- PMCID: PMC12045142
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81550
Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Atherogenic Index as Alternative Biomarkers for Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Background: The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and the atherogenic index (AI) are emerging biomarkers that have been gaining attention in diabetes management as alternatives for assessing glycemic control in clinical settings. Since direct measurement of insulin resistance is impractical in routine care, it offers a more accessible alternative with potential broad clinical application. The TyG index and AI can serve as useful substitute biomarkers and could help in the management of glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methodology: A cross-sectional study was conducted with 200 T2DM participants, divided into two groups: 100 with good glycemic control (<7.0%) and 100 with poor control (≥7.0%), based on HbA1c levels. Lipid profile and HbA1c were measured using Chem-7 (Erba Mannheim, India) and Insta Check semi-auto analyzers. TyG index, TyG-body mass index (BMI), and TyG-waist circumference (WC) were calculated using standard formulas. Statistical analysis was performed by using SPSS 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, New York, US), with p < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
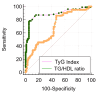
Results: Among 200 subjects, 63% were men and 37% were women. The mean age for type 2 diabetes subjects is 61.24 ± 7.25 years. The mean level of the TyG index in poor glycemic control is significantly higher (30.36 ± 5.51, p < 0.001) than that of good glycemic control (4.06 ± 0.05, p < 0.001). A significant positive correlation was observed between the TyG index and poor glycemic control. The TyG index has good predictive ability in poor glycemic control (area under the curve (AUC): 0.88; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.83-0.92). The TyG optimal cutoff is ≥5.22 with 78.22% sensitivity and 94.06% specificity.
Conclusion: The TyG index shows a significant correlation with glycemic control and could serve as a valuable supportive marker for T2DM, particularly in smaller clinical settings.
Keywords: atherogenic index; glycemic control; predictive biomarkers; triglyceride glucose index; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2025, Gajjar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Institutional Ethics Committee (Human Research) of GMERS Medical College, Vadnagar issued approval GMERS/MCV/IEC/(HR)/Approval/5619/2022. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Incidence and predictors of abnormal fasting plasma glucose among the university hospital employees in Thailand. Jiamjarasrangsi W, Lohsoonthorn V, Lertmaharit S, Sangwatanaroj S. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;79:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14:88–98. - PubMed
-
- Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–419. - PubMed
-
- Impact of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) on identifying insulin resistance among apparently healthy individuals. Saha S, Schwarz PE. J Public Health. 2017;25:505–512.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
