UFMylation orchestrates spatiotemporal coordination of RQC at the ER
- PMID: 40315331
- PMCID: PMC12047416
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv0435
UFMylation orchestrates spatiotemporal coordination of RQC at the ER
Abstract
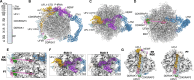
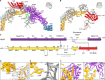
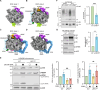
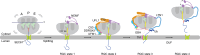
Degradation of arrest peptides from endoplasmic reticulum (ER) translocon-bound 60S ribosomal subunits via the ribosome-associated quality control (ER-RQC) pathway requires covalent modification of RPL26/uL24 on 60S ribosomal subunits with UFM1. However, the underlying mechanism that coordinates the UFMylation and RQC pathways remains elusive. Structural analysis of ER-RQC intermediates revealed concomitant binding and direct interaction of the UFMylation and RQC machineries on the 60S. In the presence of an arrested peptidyl-transfer RNA, the RQC factor NEMF and the UFM1 E3 ligase (E3UFM1) form a direct interaction via the UFL1 subunit of E3UFM1, and UFL1 adopts a conformation distinct from that previously observed for posttermination 60S. While this concomitant binding occurs on translocon-bound 60S, LTN1 recruitment and arrest peptide degradation require UFMylation-dependent 60S dissociation from the translocon. These data reveal a mechanism by which the UFMylation cycle orchestrates ER-RQC.
Figures

References
-
- Brandman O., Stewart-Ornstein J., Wong D., Larson A., Williams C. C., Li G.-W., Zhou S., King D., Shen P. S., Weibezahn J., Dunn J. G., Rouskin S., Inada T., Frost A., Weissman J. S., A ribosome-bound quality control complex triggers degradation of nascent peptides and signals translation stress. Cell 151, 1042–1054 (2012). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed A., Wang M., Bergant G., Maroofian R., Zhao R., Alfadhel M., Nashabat M., AlRifai M. T., Eyaid W., Alswaid A., Beetz C., Qin Y., Zhu T., Tian Q., Xia L., Wu H., Shen L., Dong S., Yang X., Liu C., Ma L., Zhang Q., Khan R., Shah A. A., Guo J., Tang B., Leonardis L., Writzl K., Peterlin B., Guo H., Malik S., Xia K., Hu Z., Biallelic loss-of-function variants in NEMF cause central nervous system impairment and axonal polyneuropathy. Hum. Genet. 140, 579–592 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Martin P. B., Kigoshi-Tansho Y., Sher R. B., Ravenscroft G., Stauffer J. E., Kumar R., Yonashiro R., Müller T., Griffith C., Allen W., Pehlivan D., Harel T., Zenker M., Howting D., Schanze D., Faqeih E. A., Almontashiri N. A. M., Maroofian R., Houlden H., Mazaheri N., Galehdari H., Douglas G., Posey J. E., Ryan M., Lupski J. R., Laing N. G., Joazeiro C. A. P., Cox G. A., NEMF mutations that impair ribosome-associated quality control are associated with neuromuscular disease. Nat. Commun. 11, 4625 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chu J., Hong N. A., Masuda C. A., Jenkins B. V., Nelms K. A., Goodnow C. C., Glynne R. J., Wu H., Masliah E., Joazeiro C. A. P., Kay S. A., A mouse forward genetics screen identifies LISTERIN as an E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 2097–2103 (2009). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

