Outcomes of acute myeloid leukemia with KMT2A (MLL) rearrangement: a multicenter study of TROPHY group
- PMID: 40316511
- PMCID: PMC12048516
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-025-01293-x
Outcomes of acute myeloid leukemia with KMT2A (MLL) rearrangement: a multicenter study of TROPHY group
Abstract
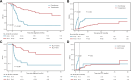
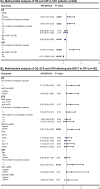
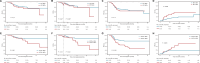
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with KMT2A rearrangement (KMT2A-r) is associated with poor prognosis, but the benefit of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) for KMT2A-r AML is unclear. We reviewed adult AML patients treated within the TROPHY group and identified 292 cases of KMT2A-r AML, 254 (87.0%) of whom achieved first complete remission (CR1) and 192 (75.6%) of CR1 patients underwent allo-HSCT. We show that allo-HSCT is an independent favorable prognostic factor in CR1 patients for both overall survival (OS) (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.56, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.45-0.69, P < 0.001) and cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) (HR = 0.01, 95% CI: 0.005-0.04, P < 0.001). Among allo-HSCT recipients, survival outcomes were comparable between patients with KMT2A::MLLT3 and those with other 11q23/KMT2A rearrangements (3-year OS: 74.3% vs. 77.5%, P = 0.97; 3-year event-free survival [EFS]: 55.2% vs. 62.2%, P = 0.34; 3-year CIR: 24.4% vs. 20.8%, P = 0.32). Both multiparameter flow cytometry-based measurable residual disease (MFC-MRD) and KMT2A-r MRD determined by quantitative PCR prior to allo-HSCT were associated with worse transplant outcomes. Multivariable analysis identified detectable KMT2A-r MRD at allo-HSCT as a significant risk factor for reduced EFS (HR = 2.46, 95% CI: 1.32-4.60, P = 0.005). These findings confirm the survival benefit of allo-HSCT in adult patients with KMT2A-r AML and underscore the prognostic value of KMT2A-r MRD prior to transplantation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular measurable residual disease before transplantation independently predicts survival and relapse risk in adult lysine methyltransferase 2a-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia.Cancer. 2025 Jan 15;131(2):e35717. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35717. Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39760486
-
Minimal residual disease monitoring and preemptive immunotherapies for frequent 11q23 rearranged acute leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Ann Hematol. 2021 May;100(5):1267-1281. doi: 10.1007/s00277-021-04488-x. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Ann Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33712867
-
Outcomes of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Adult Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia Harboring KMT2A Rearrangement and Its Prognostic Factors.Cell Transplant. 2024 Jan-Dec;33:9636897231225821. doi: 10.1177/09636897231225821. Cell Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38270130 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in KMT2A-rearranged acute leukemia].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024 May 14;45(5):514-520. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121090-20231026-00230. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38964931 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Recent Developments and Evolving Therapeutic Strategies in KMT2A-Rearranged Acute Leukemia.Cancer Med. 2024 Oct;13(20):e70326. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70326. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39428967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Byrd JC, Mrozek K, Dodge RK, Carroll AJ, Edwards CG, Arthur DC, et al. Pretreatment cytogenetic abnormalities are predictive of induction success, cumulative incidence of relapse, and overall survival in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 8461). Blood. 2002;100:4325–36. - PubMed
-
- Grimwade D, Hills RK, Moorman AV, Walker H, Chatters S, Goldstone AH, et al. Refinement of cytogenetic classification in acute myeloid leukemia: determination of prognostic significance of rare recurring chromosomal abnormalities among 5876 younger adult patients treated in the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials. Blood. 2010;116:354–65. - PubMed
-
- Grimwade D, Mrozek K. Diagnostic and prognostic value of cytogenetics in acute myeloid leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2011;25:1135–61. - PubMed
-
- Mrozek K, Heinonen K, Lawrence D, Carroll AJ, Koduru PR, Rao KW, et al. Adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia and t(9; 11)(p22; q23) have a superior outcome to patients with other translocations involving band 11q23: a cancer and leukemia group B study. Blood. 1997;90:4532–8. - PubMed
-
- Cox MC, Panetta P, Lo-Coco F, Del Poeta G, Venditti A, Maurillo L, et al. Chromosomal aberration of the 11q23 locus in acute leukemia and frequency of MLL gene translocation: results in 378 adult patients. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;122:298–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

