Phytochemical composition, antioxidant potential, and insecticidal activity of Moringa oleifera extracts against Tribolium castaneum: a sustainable approach to pest management
- PMID: 40316907
- PMCID: PMC12048962
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-06626-3
Phytochemical composition, antioxidant potential, and insecticidal activity of Moringa oleifera extracts against Tribolium castaneum: a sustainable approach to pest management
Abstract
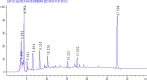
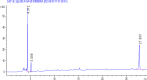
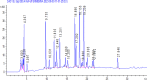
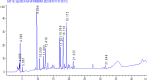
Moringa oleifera's rich phytochemical profile positions it as a promising natural alternative for sustainable pest management. This study characterizes the phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of M. oleifera extracts and, for the first time, evaluates their insecticidal potential against Tribolium castaneum (red flour beetle). Extracts from leaves, stems, roots, and seeds were prepared using ethanol, methanol, acetone, and distilled water. Phytochemical analysis identified high levels of total phenolics (7.18 µg GAE/mg DW, ethanol leaf extract), flavonoids (23.52 µg QE/mg DW, ethanol leaf extract), tannins (245.4 mg CE/g DW, acetone seed extract), saponins (13.7%, methanol leaf extract), and alkaloids (30.06 mg atropine/100 mL, water stem extract). HPLC quantification revealed abundant bioactive compounds, including phenolic acids (gallic, caffeic, chlorogenic, and ferulic acids), flavonoids (apigenin, quercetin, kaempferol), flavanols (catechin, epicatechin, procyanidin dimers), and iridoids (oleuroside), with gallic acid, quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside, and kaempferol as dominant constituents. Antioxidant assays demonstrated significant activity, with methanol root extract showing 71% DPPH inhibition and methanol stem extract exhibiting the highest total antioxidant capacity (36.12 mg GAE/g DW). Insecticidal bioassays revealed ethanol root extracts induced 90% mortality in T. castaneum within 24 h at 30% concentration, outperforming other extracts. These findings underscore M. oleifera's dual functionality as a potent bioinsecticide and antioxidant, advocating for its integration into sustainable pest management. Further research should optimize extraction protocols and field-scale formulations to enhance practical applications.
Keywords: Moringa oleifera; Tribolium castaneum; Antioxidant activity; Bioactive compounds; Flavonoids; Insecticidal properties; Natural pesticides; Phytochemicals; Sustainable pest management.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant Potential and Antibacterial Activities of Different Anatomical Parts of Hypericum cordifolium Choisy.ScientificWorldJournal. 2024 May 25;2024:8128813. doi: 10.1155/2024/8128813. eCollection 2024. ScientificWorldJournal. 2024. PMID: 38827814 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Analysis, Antimutagenic and Antiviral Activity of Moringa oleifera L. Leaf Infusion: In Vitro and In Silico Studies.Molecules. 2022 Jun 22;27(13):4017. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134017. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807260 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Antioxidants Activity of Indigenously Produced Moringa Oleifera Seeds Extracts.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Oct 15;2022:4987929. doi: 10.1155/2022/4987929. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9879751. doi: 10.1155/2024/9879751. PMID: 36325499 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A critical review on Moringa oleifera: current status, physicochemical attributes, and food industrial applications.Nat Prod Res. 2025 Apr;39(8):2293-2307. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2024.2387833. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Nat Prod Res. 2025. PMID: 39135442 Review.
-
Moringa oleifera in a modern time: A comprehensive review of its nutritional and bioactive composition as a natural solution for managing diabetes mellitus by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.Food Res Int. 2025 Feb;201:115671. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2025.115671. Epub 2025 Jan 4. Food Res Int. 2025. PMID: 39849793 Review.
Cited by
-
Pineapple by-products: A critical review of their bioactive compounds as eco-friendly pesticides in pest management.Food Chem X. 2025 May 19;28:102567. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102567. eCollection 2025 May. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40497040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zuhra F, Ali A, Ahmad F. Insecticidal activity of Mentha Royleana and Artemisia absinthium extracts against Tribolium castaneum. J Entomol Zool Stud. 2018;6(3):1234–9.
-
- Ali A, Ahmad F, Zuhra F. Efficacy of Datura Alba and Elettaria cardamomum extracts against Trogoderma granarium and Sitophilus zeamais. J Stored Prod Res. 2012;48:1–6. 10.1016/j.jspr.2011.08.002.
-
- Huang Y, Lam SL, Ho SH. Bioactivities of essential oil from Elettaria cardamomum (L.) maton. To Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky and Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). J Stored Prod Res. 2000;36(2):107–17. 10.1016/S0022-474X(99)00040-5.
-
- Mondal M, Khalequzzaman M. Insecticidal activity of Garlic (Allium sativum) and Neem (Azadirachta indica) extracts against Tribolium castaneum. J Biol Sci. 2006;6(4):732–7. 10.3923/jbs.2006.732.737.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

