Genome-wide identification of the regulatory network of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades gene families in Hevea Brasiliensis
- PMID: 40316909
- PMCID: PMC12049021
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-06615-6
Genome-wide identification of the regulatory network of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades gene families in Hevea Brasiliensis
Abstract
Background: The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MPK) cascade pathway represents a highly conserved signal transduction mechanism in plants, playing a crucial role in growth, development, and stress response. Nevertheless, systematic analysis on the MPK cascade genes in rubber trees remains unexplored.
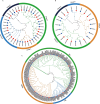
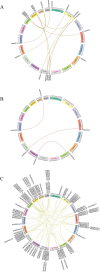
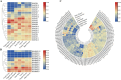
Results: We conducted a comprehensive identification of the MPK cascade gene family of Hevea brasiliensis, identifying a total of 20 HbMPKs, 13 HbMPKKs, and 167 HbMAPKKKs genes. Through phylogenetic analysis and compared to Arabidopsis MPK cascade genes, HbMPKs and HbMPKKs were categorized into categorized four subgroups with no significant expansion or contraction, while the notably expanded HbMAPKKKs were divided into three subgroups: Raf, ZIK, and MEKK. Conserved motifs, gene structure, and motif analysis further bolster the validity of phylogenetic classification. Furthermore, expression profiling analysis based on public transcriptomic data revealed that these genes were differentially expressed in various tissues and differentially regulated in response to different stresses. Among them, the genes highly expressed in latex or the upregulated genes after tapped including HbMPK8, HbMPK12, HbMPK19, HbMPKK6, HbMPKK9, HbMPKKK15, HbMPKKK21 might be related to latex development and natural rubber (NR) yield. Through yeast two-hybrid assays, we successfully pinpointed 34 pairs of HbMPKKK-HbMPKK-HbMPK interaction modules. Integrating the interaction network and gene expression patterns, 12 potential HbMPK cascade signaling modules including HbMPKKK6/41/79-HbMPKK1-HbMPK9/12/15 and HbMPKKK6/14/21/41/79-HbMPKK9-HbMPK9/15 might involve in NR production and stress responses.
Conclusions: Our study comprehensively unveils the multidimensional characteristics of the MPK cascade gene family in rubber trees and successfully identifies its core signaling cascade module, laying a crucial foundation for future in-depth exploration of the biological functions of the MPK cascade signaling module in rubber trees.
Keywords: Hevea brasiliensis; Gene family; Kinases; MPK cascade.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang M, Su J, Zhang Y, Xu J, Zhang S. Conveying endogenous and exogenous signals: MAPK cascades in plant growth and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2018;45(Pt A):1–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 202310608030/National Training Program of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates
- 325CXTD621/Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31800578/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023YFA0914800/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- CATASCXTD202413/Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences for Science and Technology Innovation Team of National Tropical Agricultural Science Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

