The predictive efficacy of dynamic level changes of plasma endothelial microparticles and plasma soluble thrombomodulin on the prognosis of severe acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 40316920
- PMCID: PMC12049059
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-025-02929-2
The predictive efficacy of dynamic level changes of plasma endothelial microparticles and plasma soluble thrombomodulin on the prognosis of severe acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the predictive efficacy of dynamic level changes of plasma endothelial microparticles (EMP) and plasma soluble thrombomodulin (sTM) on the prognosis of severe acute pancreatitis (SAP).
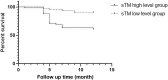
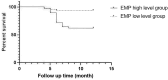
Methods: This study retrospectively selected 128 eligible SAP patients admitted to our hospital from May 2021 to April 2023. According to the final outcome, the patients were grouped as the survival group (n = 95) and death group (n = 33). The EMP, sTM and microcirculation related indexes (lactic acid level, central venous pressure (CVP), mean arterial pressure (MAP)) of SAP patients were monitored at admission, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h after admission. Pearson was adopted to analyze the correlation between EMP and sTM levels with microcirculation disorder related indicators. The levels of EMP and sTM were compared between the survival group and the death group. The EMP high level group was ≥ 150.00 ng / mL, and the EMP low level group was < 150.00 ng / mL. The sTM high-level group was ≥ 300.00 ng / mL, and the low-level group was < 300.00 ng / mL. The differences in survival curves between different groups were compared by Kaplan-Meier. AUC was used to analyze the prognostic value of EMP and sTM levels alone and in combination in SAP patients.
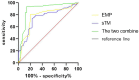
Results: Compared with admission, the levels of EMP, sTM, lactic acid and CVP in 128 SAP patients were all significantly increased at 24 h, 48 h and 72 h after admission, but the MAP was largely decreased (p < 0.05). EMP and sTM were positively correlated with lactic acid and CVP respectively, but negatively correlated with MAP (p < 0.05). The death group had much higher levels of EMP and sTM than the survival group (p < 0.05). From the perspective of 1-year survival rate, the high-level group of EMP was lower than the low-level group (p < 0.05) and the high-level group of sTM was lower than the low-level group (p < 0.05). ROC curve analysis confirmed that the sensitivity and specificity of combined detection were 92.39% and 90.54%, respectively, with the AUC of 0.903 (95%CI:0.863-0.928), which was significantly higher than that of single detection (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The levels of EMP and sTM were significantly increased in SAP patients, which were closely related to microcirculation disorders and poor prognosis. The combined detection of EMP and sTM has significant prognostic value in SAP.
Keywords: Acute pancreatitis; Dynamic monitoring; Endothelial microparticles; Microcirculation disorder; Prognosis; Soluble thrombomodulin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by The Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University. Informed consent was obtained from participants for the participation in the study and all methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Consent to participate: The patients participating in the study all agree to publish the research results. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Significance of endothelial molecular markers in the evaluation of the severity of acute pancreatitis.Surg Today. 2009;39(4):314-9. doi: 10.1007/s00595-008-3867-7. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Surg Today. 2009. PMID: 19319639
-
Soluble thrombomodulin plasma levels are an early indication of a lethal course in human acute pancreatitis.Surgery. 2002 Apr;131(4):424-32. doi: 10.1067/msy.2002.122379. Surgery. 2002. PMID: 11935133
-
Elevated B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and soluble thrombomodulin (sTM) indicates severity and poor prognosis of sepsis.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 May;10(5):5561-5567. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1048. Epub 2021 May 18. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34044565
-
Prognostic value of red blood cell distribution width for severe acute pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug 28;25(32):4739-4748. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4739. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31528098 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction and outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Microvasc Res. 2021 Nov;138:104224. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2021.104224. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Microvasc Res. 2021. PMID: 34273359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lugo-Gavidia LM, Burger D, Matthews VB, Role of Microparticles in Cardiovascular Disease: Implications for Endothelial Dysfunction, Thrombosis, and Inflammation., Hypertension et al. Dallas, Tex: (1979). 2021;77(6):1825–1844. - PubMed
-
- Lu Y, Li L, Yan H, et al. Endothelial microparticles exert differential effects on functions of Th1 in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(6):5396–404. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

