The quality of life and related factors in older adults with possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia in rural areas of Xinjiang, China: a cross sectional study
- PMID: 40316923
- PMCID: PMC12046794
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-025-05950-5
The quality of life and related factors in older adults with possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia in rural areas of Xinjiang, China: a cross sectional study
Abstract
Background: Studies have shown that sarcopenia prevalence in the Chinese population aged over 60 years was 14%. The quality of life of older adults with sarcopenia has drawn increasing attention. Sarcopenia-related quality of life has not been well studied. We explored the quality of life of patients with sarcopenia and the related influencing factors in Xinjiang.
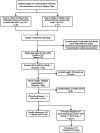
Methods: This study was conducted from July-September 2023 in the northern and southern regions of Xinjiang, China. Possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia were diagnosed according to the AWGS 2019. The Sarqol® questionnaire was used to evaluate quality of life. A linear regression model with a stepwise method was used to identify quality-of-life-associated factors for possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia.
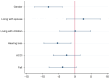
Results: A total of 987 older adults were enrolled,18.5% had possible sarcopenia, and 15.1% had sarcopenia. Quality of life scores: possible sarcopenia 26.46-92.55 (56.31 ± 14.69), sarcopenia 30.74-90.93 (56.91 ± 13.45).The indicators for which the difference analysis were meaningful, in the group with possible sarcopenia are gender, inhabiting information, ACCI score, hearing loss, social support level and self-rated risk of falling. In the sarcopenia group are gender, ACCI score, hearing loss, vision loss, self-rated health status, number of remaining teeth, self-rated risk for falling, and dysphagia status. The risk factors for quality of life in patients with possible sarcopenia were gender and hearing loss, whereas self-rated of general health, self-rated of poor health, self-rated of very poor health and falls were risk factors in the sarcopenia group.
Conclusion: This study focused on quality of life and factors in older adults with possible sarcopenia or sarcopenia. The research results showed that in order to prevent the decline in the quality of life of older adults with sarcopenia, it is very important to regularly examine the oral health status of the older adults, prevent the occurrence of chronic diseases.Multimodal interventions address common sensory impairments.Carry out aging-friendly renovation of the home environment and conduct balance training to prevent the occurrence of falls among the older adults.
Keywords: Possible sarcopenia; Quality of life; Sarcopenia; Sarqol questionnaire.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Study supervision: All the authors approved the final article. Conflict of interest: All the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to declare. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted according to the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki; all procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB number: XJYKDXR20220725029) of Xinjiang Medical University, China. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations between the quality of life in sarcopenia measured with the SarQoL® and nutritional status.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021 Jan 22;19(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01619-2. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021. PMID: 33482832 Free PMC article.
-
Association between sarcopenia and falls in Chinese older adults: Findings from the China health and retirement longitudinal study.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 12;20(6):e0326193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326193. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40504826 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcopenia prevalence and associated factors among older Chinese population: Findings from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 4;16(3):e0247617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247617. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33661964 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of sarcopenia and risk factors in the older adult in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Public Health. 2024 Aug 5;12:1415398. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1415398. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39161853 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental and behavioural interventions for reducing physical activity limitation and preventing falls in older people with visual impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 3;9(9):CD009233. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009233.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32885841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen L-K, Woo J, Assantachai P, et al. Asian working group for sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment[J]. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(3):300–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2022E02119/Science and Technology Aid to Xinjiang Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2022E02119/Science and Technology Aid to Xinjiang Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2022E02119/Science and Technology Aid to Xinjiang Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2022E02119/Science and Technology Aid to Xinjiang Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2022E02119/Science and Technology Aid to Xinjiang Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2022E02119/Science and Technology Aid to Xinjiang Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2022E02119/Science and Technology Aid to Xinjiang Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2022E02119/Science and Technology Aid to Xinjiang Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2023D01C217/Natural Science Youth Fund Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2023D01C217/Natural Science Youth Fund Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2023D01C217/Natural Science Youth Fund Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2023D01C217/Natural Science Youth Fund Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2023D01C217/Natural Science Youth Fund Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2023D01C217/Natural Science Youth Fund Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2023D01C217/Natural Science Youth Fund Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- 2023D01C217/Natural Science Youth Fund Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
- XYD2024C06/Xinjiang Medical University Research and Innovation Team Project
- XYD2024C06/Xinjiang Medical University Research and Innovation Team Project
- XYD2024C06/Xinjiang Medical University Research and Innovation Team Project
- XYD2024C06/Xinjiang Medical University Research and Innovation Team Project
- XYD2024C06/Xinjiang Medical University Research and Innovation Team Project
- XYD2024C06/Xinjiang Medical University Research and Innovation Team Project
- XYD2024C06/Xinjiang Medical University Research and Innovation Team Project
- XYD2024C06/Xinjiang Medical University Research and Innovation Team Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical