Indirect Comparisons of Efficacy of Zanubrutinib Versus Orelabrutinib in Patients with R/R MCL: An Extended Follow-up Analysis
- PMID: 40317419
- PMCID: PMC12085368
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-025-03202-x
Indirect Comparisons of Efficacy of Zanubrutinib Versus Orelabrutinib in Patients with R/R MCL: An Extended Follow-up Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Our previous study has suggested a favorable progression-free survival (PFS) with zanubrutinib over orelabrutinib in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (R/R MCL). Here, we conducted an updated analysis to indirectly compare the long-term efficacy between zanubrutinib and orelabrutinib in patients with R/R MCL.
Methods: Individual patient data from the zanubrutinib study were adjusted to match the patient population profile of the orelabrutinib study. An unanchored matching-adjusted indirect comparison (MAIC) was performed to adjust for effect modifiers and prognostic variables. The efficacy outcomes included investigator-assessed PFS, overall survival (OS), and overall response rate (ORR). Response evaluations were only computed tomography (CT)-based assessments in the orelabrutinib study, while positron emission tomography (PET)- and CT-based assessment were both performed in the zanubrutinib study. The comparison of PFS assessed by CT between zanubrutinib and orelabrutinib was the primary result.
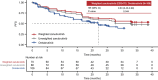
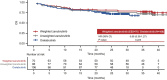
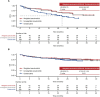
Results: After matching, the baseline characteristics were balanced between zanubrutinib and orelabrutinib, with an effective sample size of 70 in the zanubrutinib study. PFS assessed by CT was significantly longer in the zanubrutinib study vs. the orelabrutinib study (median PFS, not reached vs. 22.0 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.54, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.34-0.86; P = 0.009). With longer follow-up, OS continued to trend favorably for zanubrutinib, with OS rate at 24 months numerically higher (83.7% vs. 74.3%); no statistical difference was observed (HR 0.68, 95% CI 0.36-1.27; P = 0.223). ORR was numerically higher in the zanubrutinib study (85.5% vs. 82.1%; odds ratio 1.28, 95% CI 0.56-2.94; P = 0.556).
Conclusion: MAIC results demonstrated that zanubrutinib had significantly longer PFS compared with orelabrutinib in the treatment of patients with R/R MCL.
Keywords: Matching-adjusted indirect comparison; Orelabrutinib; Progression-free survival; Relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma; Zanubrutinib.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: The authors Lijuan Deng, Yuqin Song, Keshu Zhou, Dengju Li, Jianda Hu, Dehui Zou, Sujun Gao, Haiyan Yang, Huilai Zhang, Jie Ji, Wei Xu, Ru Feng, Jie Jin, Fangfang Lv, Cheng Fang, Sheng Xu, Jun Zhu have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Ethical Approval: Ethics committee approval was not required for the study. For the zanubrutinib trial, the study was designed and monitored in accordance with sponsor procedures in compliance with the ethical principles of Good Clinical Practice, International Conference on Harmonization guidelines, the Declaration of Helsinki, and applicable local regulatory requirements. All patients provided written informed consent. The protocol, any amendments, and informed consent forms were reviewed and approved by the institutional review boards/independent ethics committees. For the orelabrutinib trial, all patients provided written informed consent [13].
Figures

Similar articles
-
Indirect comparisons of efficacy of zanubrutinib versus orelabrutinib in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma or relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma.Invest New Drugs. 2023 Aug;41(4):606-616. doi: 10.1007/s10637-023-01376-1. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Invest New Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37420136 Free PMC article.
-
Matching-adjusted indirect comparison of acalabrutinib versus ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma.J Med Econ. 2024 Jan-Dec;27(1):1552-1557. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2024.2422227. Epub 2024 Dec 5. J Med Econ. 2024. PMID: 39461001 Clinical Trial.
-
Matching-adjusted Indirect Comparisons of the Efficacy and Safety of Acalabrutinib Versus Other Targeted Therapies in Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma.Clin Ther. 2019 Nov;41(11):2357-2379.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.09.012. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Clin Ther. 2019. PMID: 31699438
-
Zanubrutinib monotherapy in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: a pooled analysis of two clinical trials.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Oct 14;14(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01174-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34649571 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Current Role and Emerging Evidence for Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Mantle Cell Lymphoma.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2020 Oct;34(5):903-921. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2020.06.007. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 32861286 Review.
References
-
- Hillmen P, Brown JR, Eichhorst BF, et al. ALPINE: zanubrutinib versus ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Future Oncol. 2020;16:517–23. - PubMed
-
- Song Y, Zhou K, Zou D, et al. Treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma with zanubrutinib, a selective inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:4216–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

