Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor Predicts Survival and Hepatic Decompensation in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 40317602
- PMCID: PMC12046945
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.70121
Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor Predicts Survival and Hepatic Decompensation in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background and aims: The introduction of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) based therapies has significantly improved the prognosis of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the variable treatment response and the uncertain benefit in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis emphasise the urgent need for prognostic and predictive biomarkers guiding patient selection. The soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) is strongly associated with inflammation, liver cirrhosis and various types of cancer. In this study, we investigated suPAR as a potential novel biomarker in patients with unresectable HCC.
Methods: This multicenter retrospective study, conducted at three German tertiary care centers, included 90 patients with unresectable HCC and suPAR measurements prior to and during atezolizumab/bevacizumab therapy. Patients with liver cirrhosis without HCC (n = 235) and non-cirrhotic patients with other gastrointestinal tumours (n = 155) were selected as control cohorts.
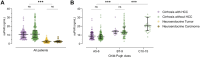
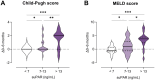
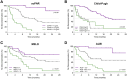
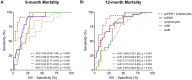
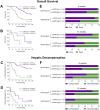
Results: Median suPAR levels were significantly higher in patients with liver cirrhosis compared to non-cirrhotic cancer patients. A strong association with parameters of liver function, but not with HCC characteristics, was observed. In patients with HCC receiving atezolizumab/bevacizumab, suPAR was the most accurate independent predictor of hepatic decompensation and overall survival (OS). In addition, suPAR was able to stratify the risk of hepatic decompensation within the different Child-Pugh classes.
Conclusions: SuPAR represents a promising novel biomarker in patients with HCC treated with ICI-based therapies and bears the potential to guide the selection of antitumoral systemic therapies in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis.
Keywords: atezolizumab; bevacizumab; biomarker; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR); survival.
© 2025 The Author(s). Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R. L., et al., “Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries,” CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 71, no. 3 (2021): 209–249. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J., Chan S. L., Galle P. R., Rimassa L., and Sangro B., “Systemic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An EASL Position Paper,” Journal of Hepatology 75, no. 4 (2021): 960–974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

