Increased burden of rare risk variants across gene expression networks predisposes to sporadic Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 40317721
- PMCID: PMC12258067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115636
Increased burden of rare risk variants across gene expression networks predisposes to sporadic Parkinson's disease
Abstract
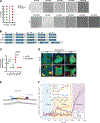
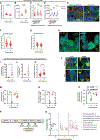
Alpha-synuclein (αSyn) is an intrinsically disordered protein that accumulates in the brains of patients with Parkinson's disease (PD). Through a high-throughput screen, we recently identified 38 genes whose knockdown modulates αSyn propagation. Here, we show that, among those, TAX1BP1 regulates how αSyn interacts with lipids, and ADAMTS19 modulates how αSyn phase separates into inclusions, adding to the growing body of evidence implicating those processes in PD. Through RNA sequencing, we identify several genes that are differentially expressed after knockdown of TAX1BP1 or ADAMTS19 and carry an increased frequency of rare risk variants in patients with PD versus healthy controls. Those differentially expressed genes cluster within modules in regions of the brain that develop high degrees of αSyn pathology. We propose a model for the genetic architecture of sporadic PD: increased burden of risk variants across genetic networks dysregulates pathways underlying αSyn homeostasis and leads to pathology and neurodegeneration.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; Lewy bodies; Parkinson’s disease; alpha-synuclein; chloroquine; genomics; lipid droplets; lipids; liquid-liquid phase separation; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.M.M. is an inventor of filed and issued patents related to α-synuclein. M.M.M. is a founder of MentiNova, Inc. E.K. is a member of the EMBO Scientific Exchange Grants Advisory Board.
Figures





Update of
-
Increased burden of rare risk variants across gene expression networks predisposes to sporadic Parkinson's disease.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 1:2024.08.30.610195. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.30.610195. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2025 May 27;44(5):115636. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115636. PMID: 39257816 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Kim TE, Newman AJ, Imberdis T, Brontesi L, Tripathi A, Ramalingam N, Fanning S, Selkoe D, and Dettmer U (2021). Excess membrane binding of monomeric alpha-beta- and gamma-synuclein is invariably associated with inclusion formation and toxicity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 30, 2332–2346. 10.1093/hmg/ddab188. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shahmoradian SH, Lewis AJ, Genoud C, Hench J, Moors TE, Navarro PP, Castaño-Díez D, Schweighauser G, Graff-Meyer A, Goldie KN, et al. (2019). Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 1099–1109. 10.1038/s41593-019-0423-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

