Synthesis of 2-Substituted Adenosine Triphosphate Derivatives and their use in Enzymatic Synthesis and Postsynthetic Labelling of RNA
- PMID: 40317833
- PMCID: PMC12177693
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202500241
Synthesis of 2-Substituted Adenosine Triphosphate Derivatives and their use in Enzymatic Synthesis and Postsynthetic Labelling of RNA
Abstract
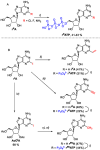
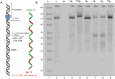
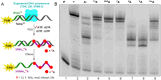
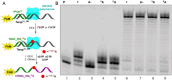
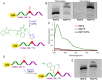
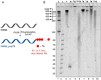
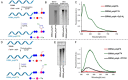
A series of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) derivatives bearing chloro, fluoro, amino, methyl, vinyl, and ethynyl groups at position 2 are synthesized and tested as substrates for RNA and DNA polymerases. The modified nucleotides work well in in vitro transcription with T7 RNA polymerase and primer extension (PEX) using engineered DNA polymerases (TGK, 2M) except for the bulkier 2-vinyl- and 2-ethynyl-ATP derivatives that give truncated products. However, in single nucleotide incorporation followed by PEX, they still can be used for site-specific incorporation of reactive modifications into RNA that can be further used for postsynthetic labeling through thiol-ene or Cu-catalyzed alkyne-azide cycloadditions reactions. All modified ATPs work in polyadenylation catalyzed by poly(A) polymerase to form long 3'-polyA tails containing the modifications that also can be used for labeling.
Keywords: DNA polymerases; RNA polymerases; click reactions; nucleosides triphosphates; nucleotides; polyA polymerase; thiol‐ene addition.
© 2025 The Author(s). ChemBioChem published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Androsavich J. R., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2024, 23, 421. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

