Beyond the injection: delivery systems reshaping retinal disease management
- PMID: 40319468
- PMCID: PMC12360407
- DOI: 10.1080/14656566.2025.2496424
Beyond the injection: delivery systems reshaping retinal disease management
Abstract
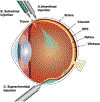
Introduction: Intravitreal injections remain the standard for treating common retinal diseases including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic macular edema (DME) and diabetic retinopathy. However, frequent administration creates significant treatment burden due to limited drug half-life and the chronic nature of these conditions.
Areas covered: This review summarizes emerging drug delivery techniques and therapies for retinal disease that have achieved FDA approval within the past five years or have advanced to Phase 3 development, including intravitreal sustained-release platforms and alternative delivery routes (suprachoroidal, subretinal, topical, and subcutaneous). Specific innovations discussed include the ranibizumab port delivery system, EYP-1901 (Duravyu, vorolanib implant), KSI-301 (tarcocimab tedromer), KSI-501, OTX-TKI (Axpaxli, axitinib implant), 4D-150, revakinagene taroretcel-lwey (Encelto, NT-501, encapsulated cell therapy), Xipere (triamcinolone acetonide injectable suspension), AU-011 (belzupacap sarotalocan targeted delivery), ABBV-RGX-314, elamipretide, and OCS-01 (high concentration dexamethasone).
Expert opinion: Promising innovations include sustained-release intravitreal implants, topical and subcutaneous delivery systems, and targeted methods like suprachoroidal and subretinal injections, each with unique advantages and limitations. Challenges include overcoming the blood-retinal barrier, surgical complications with implantable devices, and ensuring patient adherence. Advances in smart delivery systems, drug formulations, and predictive models, alongside interdisciplinary collaboration, will be crucial in achieving personalized, effective, and sustainable retinal therapies.
Keywords: Drug delivery; gene therapy; intravitreal injection; port delivery system; retina; subretinal delivery; suprachoroidal delivery; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest
T Ciulla declares consultancy and stock options for Clearside Bio, consultancy and stock options for Nanoscope, consultancy for Ocuphire/Opus and consultancy, stock options, and employment through to Feb 2025 for Viridian Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
-
Ciulla TA, Hussain RM, Taraborelli D, et al. Longer-term anti-VEGF therapy outcomes in neovascular age-related macular degeneration, diabetic macular edema, and vein occlusion-related macular edema: clinical outcomes in 130 247 eyes. Ophthalmol Retina. 2022;6(9):796–806. doi: 10.1016/j.oret.2022.03.021
•Large retrospective study demonstrating that longer-term real-world anti-VEGF outcomes are inferior to those in randomized clinical trials.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
