Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Spexin on Acetic Acid‑Induced Colitis in Rats via Modulating the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway
- PMID: 40320895
- PMCID: PMC12050913
- DOI: 10.1002/jbt.70285
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Spexin on Acetic Acid‑Induced Colitis in Rats via Modulating the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway
Abstract
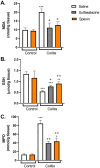
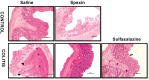
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease characterized by inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the colon and rectum. Spexin is a novel peptide with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. This study aims to elucidate the therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms of spexin in mitigating acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Male Sprague Dawley rats were assigned to control (n = 14) and colitis (n = 21) groups. Colitis was induced via 5% acetic acid (AA) administration (1 mL, intrarect). Post-induction, rats received subcutaneous saline (1 mL/kg), spexin (50 µg/kg/day), or oral sulfasalazine (500 mg/kg) for 5 days. Control groups received saline or spexin. After 24 h of the final treatment, colons were evaluated macroscopically, and levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-18 were determined by ELISA, oxidative stress markers myeloperoxidase (MPO), malondialdehyde (MDA) and glutathione (GSH) levels were measured spectrophotometrically and NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3), nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), caspase-1 proteins were analyzed with Western Blot alongside histopathological assessments. Colitis induction significantly elevated macroscopic damage scores, stool consistency, inflammatory cytokines, MDA, MPO, and NLRP3, NF-κB, caspase-1, while reducing GSH levels (p < 0.001-0.01). Microscopic evaluations confirmed increased necrosis, submucosal edema, and inflammatory cell infiltration (p < 0.001). Spexin reversed these effects by enhancing GSH levels (p < 0.01), reducing macroscopic/microscopic scores, cytokines, MDA, and MPO levels (p < 0.05-0.001), and suppressing NLRP3, NF-κB, and caspase-1 activation (p < 0.01-0.001). For the first time that spexin ameluates acetic acid-induced colitis in rats by modulating the NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway, reducing oxidative damage, enhancing antioxidant capacity, and suppressing inflammation.
Keywords: NLRP3; inflammation; oxidative damage; spexin; ulcerative colitis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
-
Unraveling the Protective Effect of Hesperetin In Experimentally Induced Colitis: Inhibition of NF-κB and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025 Mar;39(3):e70229. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70229. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40096268
-
Canna x generalis L.H. Bailey rhizome extract ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via modulating intestinal mucosal dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and TLR4/ NF-ҡB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113670. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113670. Epub 2020 Dec 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33301917
-
Regulation of NLRP3/TRIM family signaling in gut inflammation and colorectal cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025 Apr;1880(2):189271. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2025.189271. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39864469 Review.
-
The Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs): A Novel Therapeutic Approach to Atherosclerosis Pathophysiology.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 31;18(2):197. doi: 10.3390/ph18020197. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006011 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between perivascular adipose tissue and adipocyte-derived peptide in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Aug 13;24(1):332. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02863-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40804626 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arya H., Dass R., Chopra B., et al., “An Update on Herbal Products for the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease,” Anti‐Inflammatory & Anti‐Allergy Agents in Medicinal Chemistry 22, no. 1 (2023): 1–9. - PubMed
-
- Dai N., Yang X., Pan P., et al., “Bacillus Paralicheniformis, an Acetate‐Producing Probiotic, Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis via Protecting the Intestinal Barrier and Regulating the NLRP3 Inflammasome,” Microbiological Research 287 (2024): 127856. - PubMed
-
- Perera A. P., Sajnani K., Dickinson J., Eri R., and Körner H., “NLRP3 Inflammasome in Colitis and Colitis‐Associated Colorectal Cancer,” Mammalian Genome 29 (2018): 817–830. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

