Metabolomics and proteomics analyses reveal the role of the glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway in unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
- PMID: 40321821
- PMCID: PMC12049100
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19317
Metabolomics and proteomics analyses reveal the role of the glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway in unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion
Abstract
Background: Unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion (URSA) is a complex pregnancy complication with a high miscarriage rate. Incomprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanism in URSA also leads to a lack of effective treatment methods. Hence, the current study aimed to explore the underlying pathogenesis of URSA applying metabonomic and bioinformatics analysis.
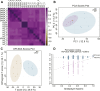
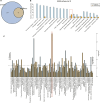
Methods: The decidual tissues of eight URSA samples and eight normal pregnancy (normal control, NC) samples were collected for liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis using the Progenesis QI metabolomics software. The orthogonal partial least squares discrimination analysis (OPLS-DA) and the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) were employed for differential metabolite analysis and pathway enrichment analysis, respectively. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway topological analysis was performed to rank the importance of pathways involved in URSA, and differential proteins were identified based on fold change difference. Finally, a metabolic network was visualized by the Cytoscape tool.
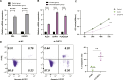
Results: After LC-MS analysis and quality control, samples in the same group showed high consistency and reliability. Differential metabolites between NC and URSA groups were mainly enriched to five biological processes, with glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway containing the greatest number of differential metabolites. KEGG enrichment analysis showed significant differences in glycerophospholipid metabolism, bile secretion, and choline metabolism pathways, with glycerophospholipid metabolism showing a higher pathway importance. Proteome and metabolome analysis revealed a total of 65 overlapping pathways involved in the differential proteins and differential metabolites, and finally PLD1, CHPT1 and PLA2G2A were identified as the key genes in glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway.
Conclusion: LC-MS analysis revealed that glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway and its three key genes were crucially involved in URSA progression, providing novel insights into the treatment strategy of URSA.
Keywords: Bioinformatics technology; Glycerophospholipid metabolism; Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry; Orthogonal partial least squares discrimination analysis; Unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion.
©2025 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Banthiya S, Kalms J, Galemou Yoga E, Ivanov I, Carpena X, Hamberg M, Kuhn H, Scheerer P. Structural and functional basis of phospholipid oxygenase activity of bacterial lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2016;1861(11):1681–1692. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.08.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cuny H, Rapadas M, Gereis J, Martin E, Kirk RB, Shi H, Dunwoodie SL. NAD deficiency due to environmental factors or gene-environment interactions causes congenital malformations and miscarriage in mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2020;117(7):3738–3747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1916588117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

