Instruments for Assessing Patient Independence in Self-Care: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 40321885
- PMCID: PMC12050024
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S510034
Instruments for Assessing Patient Independence in Self-Care: A Scoping Review
Abstract
Aim: Measuring patients' independence in caring for themselves is essential in nursing care, especially in the internal medicine room environment. Many patients with various conditions need help in self-care.
Objective: To identify the right instrument to measure patients' level of independence in performing self-care.
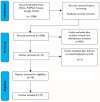
Methods: The scoping review uses the PICO framework through PubMed, Science Direct, and Scopus databases.
Results: Nine instruments/measuring tools can be used to measure the level of independence of patients in self-care, namely CDS, Barthel Index and MBI (Modified Barthel Index), SCHFI, ECOG, Self-care ability questionnaire, DCTAQ, and Revised Summary of Diabetes Self-Care.
Conclusion: Some instruments have various assessment methods and scores but can provide helpful information for health practitioners to assess patient independence. The instrument has been tested for validity and reliability in multiple studies. No instrument is absolutely the best, as each instrument has its advantages according to its context and purpose of use.
Keywords: internal medicine; measuring instruments; patient Independence level; self-care.
© 2025 Eriyani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Sugiharti N, Rohita T, Rosdiana N, Nurkholik D. The relationship between family support and the level of independence in self-care (Self-Care) in stroke patients in the Ciamis sub-district area. J Keperawatan Galuh. 2020;2:79. doi: 10.25157/jkg.v2i2.4538 - DOI
-
- Safitri R, Ulmy Mahmud N, Sulaeman U. The relationship between health literacy and self-care management of diabetes mellitus patients at Tenriawaru Hospital, Bone Regency. Wind Public Heal J. 2022;3:635–646. doi: 10.33096/woph.v3i4.51 - DOI
-
- Navidian A, Yaghoubinia F, Ganjali A, Khoshsimaee S. The effect of self-care education on the awareness, attitude, and adherence to self-care behaviors in hospitalized patients due to heart failure with and without depression. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0130973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130973 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources