Determinants of Medication Non-Adherence among Productive-Aged Hypertensive Patients in Indonesia: A Secondary Data Analysis of Basic Health Research Database 2018
- PMID: 40321908
- PMCID: PMC12045869
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v54i4.18415
Determinants of Medication Non-Adherence among Productive-Aged Hypertensive Patients in Indonesia: A Secondary Data Analysis of Basic Health Research Database 2018
Abstract
Background: Medication non-adherence in hypertensive patients induced disease progressivity. Several factors contribute to non-adherence to treatment, such as multidrug prescription, the relationship between doctors and patients, and barriers in health services. We aimed to analyze determinants of medication non-adherence in productive-aged hypertensive patients in Indonesia.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among 58,148 respondents across Indonesia. Covariates are gender, age, education, occupation, residence, smoking status, family member, and history of stroke, cardiovascular and diabetes mellitus. Chi-square and Binary Logistic were performed using SPSS version 21.
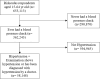
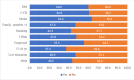
Results: More than half of the 58,148 hypertension patients in Indonesia (53.9%) are not taking their medication regularly. Chi-square analysis found that male gender, age groups (25 to 34, 35 to 44, 45 to 55, 56 to 64), graduated senior high school, employed workers, living in urban, smokers, four family members, and disease history correlated with non-adherence to treatment. However, Binary Logistic is obtained that age groups age groups (25 to 34, 35 to 44, 45 to 55 and 56 to 64; AOR=1.251, 1.609, 2.179, 2.424, respectively), employed workers (AOR=0.912), urban lived (AOR=1.085), smokers (AOR=0.853), more than four family members (AOR=1.146), stroke history (AOR=1.793), cardiovascular history (AOR=1.623), and diabetes mellitus history (AOR=1.489) found their significance level at 0.00. Two variables, gender and education, are not of significant.
Conclusion: Medication non-adherence in hypertensive patients has multifactorial aspects, such as in this study, including age, employed workers, living in urban areas, smokers, more prominent family members, and the history of the disease.
Keywords: Hypertension; Indonesia; Medication non-adherence; Riset kesehatan dasar (RISKESDAS).
Copyright© 2025 Kuntari et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Bloch MJ. (2016). The worldwide prevalence of hypertension exceeds 1.3 billion. J Am Soc Hypertens, 10(10):753–754. - PubMed
-
- PAHO . Measure your blood pressure accurately, control it, live longer! [internet]. [Cited 2023 May 12]. Available from https://www.paho.org/en/events/measure-your-blood-pressure-accurately-co...
-
- Khasanah DN. (2022). The risk factors of hypertension in Indonesia (Data study of Indonesian family life survey 5). Journal of Public Health Research and Community Health Development, 5(2):80–89.
-
- WHO . Prevalence of hypertension among adults aged 30–79 yr [Internet]. [cited 2023 Sep 16]. Available from: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/indicators/indicator-details/GHO/preva...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources