The Emerging Role of Adropin in Neurological Health: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40321920
- PMCID: PMC12045872
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v54i4.18407
The Emerging Role of Adropin in Neurological Health: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Adropin, a peptide hormone has role in various various physiological processes, including metabolic regulation and cardiovascular health. This systematic review aimed to synthesize findings from observational studies on the involvement of adropin in neurological disorders and cognitive performance.
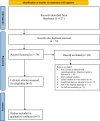
Methods: An extensive literature search was conducted across PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, CORE, and Google Scholar using terms such as "adropin," "Neurological Disorders," "cognitive function," "Alzheimer's disease," "Parkinson's disease," "cognition," and "brain function." Studies published from 2020 to 2024 were selected and reviewed. The search and selection process adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Out of 127 screened articles, 5 met the inclusion criteria for this review.
Results: The combined research findings suggest a consistent link between decreased adropin levels and a range of neurological disorders and cognitive impairments. In particular, reduced adropin levels were seen in individuals with dementia, cognitive impairment, bipolar disorder, Parkinson's disease, and multiple sclerosis. These findings highlight adropin's potential role in modulating neurological health and cognitive function.
Conclusion: This systematic review underscores the importance of adropin in neurological health and its potential as a therapeutic agent. Based on the observed connections, adropin might serve as a new focus for treating neurological disorders, prompting the need for more research and trials.
Keywords: Adropin; Cognitive function; Neurological disorders; Neuroprotection; Systematic review.
Copyright© 2025 Sivakumar et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adropin: A crucial regulator of cardiovascular health and metabolic balance.Metabol Open. 2024 Jun 27;23:100299. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2024.100299. eCollection 2024 Sep. Metabol Open. 2024. PMID: 39045137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
The levels of adropin and its therapeutic potential in diabetes.J Endocrinol. 2025 Feb 18;265(1):e240117. doi: 10.1530/JOE-24-0117. Print 2025 Apr 1. J Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 39888316 Review.
-
Adropin- A Novel Biomarker of Heart Disease: A Systematic Review Article.Iran J Public Health. 2016 Dec;45(12):1568-1576. Iran J Public Health. 2016. PMID: 28053922 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
