Feasibility and Safety of Anlotinib Plus Docetaxel versus Docetaxel Monotherapy in Patients with Previously Immunotherapy-Treated NSCLC: A Retrospective Exploratory Study
- PMID: 40321936
- PMCID: PMC12048712
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S521360
Feasibility and Safety of Anlotinib Plus Docetaxel versus Docetaxel Monotherapy in Patients with Previously Immunotherapy-Treated NSCLC: A Retrospective Exploratory Study
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of anlotinib plus docetaxel in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have previously treated with immunotherapy.
Methods: This retrospective analysis was conducted on 86 previously immunotherapy-treated patients with advanced NSCLC from December 2018 to October 2024 in clinical practice. Those who received anlotinib plus docetaxel were assigned to experimental group (EG, N=43), while those who were treated with docetaxel monotherapy were deemed as control group (CG, N=43) in clinical practice. Efficacy and safety of both regimens were compared with regular follow-up for survival data collection. The primary endpoints included overall survival (OS) and secondary endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR).
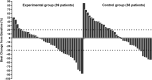
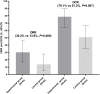
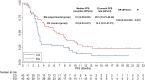
Results: ORR in the experimental and control groups was 30.2% (95% CI: 17.2-46.1%) and 13.9% (95% CI: 5.3-27.9%), respectively, showing a trend towards significance (P=0.069). DCR was significantly higher in the EG at 79.1% (95% CI: 63.9-89.9%) compared to 51.2% (95% CI: 35.5-66.7%) in the CG (P=0.007). After a median follow-up of 12.8 and 8.5 months, respectively, the median PFS was 6.5 months (95% CI: 4.08-8.92) in the EG, compared to 2.9 months (95% CI: 2.53-3.27) in the CG (P=0.019). The median OS was 13.5 months (95% CI: 10.49-16.51) in the EG, compared to 9.2 months (95% CI: 5.73-12.67) in the CG (P=0.007). Adverse events of all grades occurred in 93.0% of patients in the EG and 83.7% in the CG. Grade 3 or above adverse events were detected in 51.2% and 44.2%, respectively, with similar safety profiles between the groups.
Conclusion: Anlotinib plus docetaxel demonstrated preliminary efficacy and a tolerable safety profile in patients with previously immunotherapy-treated advanced NSCLC, providing a potential therapeutic option in the post-immunotherapy setting. The conclusion should be confirmed in prospective clinical trials subsequently.
Keywords: NSCLC; anlotinib; docetaxel; efficacy; previously immunotherapy-treated; safety.
© 2025 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Luo XC, Tang P, Zhong PX. Analysis of the effects of bevacizumab combined with chemoradiotherapy on VEGF, bFGF, and Let-7 levels in non-small cell lung cancer and the factors influencing therapeutic efficacy: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Gen Med. 2024;17:5727–5735. doi: 10.2147/ijgm.s488849 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

