This is a preprint.
The Dissipation Theory of Aging: A Quantitative Analysis Using a Cellular Aging Map
- PMID: 40321941
- PMCID: PMC12047931
The Dissipation Theory of Aging: A Quantitative Analysis Using a Cellular Aging Map
Update in
-
The dissipation theory of aging: a quantitative analysis using a cellular aging map.NPJ Aging. 2025 Oct 9;11(1):86. doi: 10.1038/s41514-025-00277-2. NPJ Aging. 2025. PMID: 41068147 Free PMC article.
Abstract
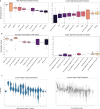
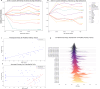
We propose a new theory for aging based on dynamical systems and provide a data-driven computational method to quantify the changes at the cellular level. We use ergodic theory to decompose the dynamics of changes during aging and show that aging is fundamentally a dissipative process within biological systems, akin to dynamical systems where dissipation occurs due to non-conservative forces. To quantify the dissipation dynamics, we employ a transformer-based machine learning algorithm to analyze gene expression data, incorporating age as a token to assess how age-related dissipation is reflected in the embedding space. By evaluating the dynamics of gene and age embeddings, we provide a cellular aging map (CAM) and identify patterns indicative of divergence in gene embedding space, nonlinear transitions, and entropy variations during aging for various tissues and cell types. Our results provide a novel perspective on aging as a dissipative process and introduce a computational framework that enables measuring age-related changes with molecular resolution.
Keywords: aging; dissipation; dynamical systems; language modeling; multimodal foundation model; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
