Photodynamic particle pump in microfluidic systems
- PMID: 40321990
- PMCID: PMC12047725
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.555270
Photodynamic particle pump in microfluidic systems
Abstract
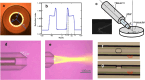
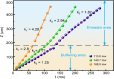
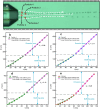
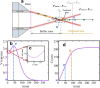
Micro-pumps are widely used in biomedical equipment such as flow cytometry. In micro-flow systems, pumps are usually the main tool and means to control the flow rate of liquid. Controlling the particle movement in micro-flow is always a difficult problem in a mixed fluid of liquid and particles. In this paper, we propose a new type of photodynamic particle pump based on annular-core hollow-center fiber. The laser is coupled into the annular core by fused tapering optical fiber and welding at the cone point. A femtosecond laser processing system is used to process microscopic holes on the side of the fiber to achieve particle injection. The laser will converge to form a conical shell light field after passing through the cone, and the speed of the particles increases after passing through the conical shell light field, thus forming a particle pump. The experimental results show that the particle velocity increases with the increase of laser power at low injection pressure. In the case of constant power, the flow rate is independent of the injection pressure, and the particle velocity in the micro-flow system is controlled. It has important value and application prospects for particle acceleration control of microfluidic chip systems and cell manipulation and sorting in the microbiological field.
© 2025 Optica Publishing Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Lashkaripour A., Silva R., Densmore D., “Desktop micromilled microfluidics,” Microfluid. Nanofluid. 22(3), 31 (2018). 10.1007/s10404-018-2048-2 - DOI
-
- Gao Y., Wu M., Lin Y., et al. , “Acoustic bubble-based bidirectional micropump,” Microfluid. Nanofluid. 24(4), 29 (2020). 10.1007/s10404-020-02334-6 - DOI
-
- Ikeda M., Imai S., “Basic study of micro-pumps for medication driven by chemical reactions,” IEICE Trans. Electron. 106(6), 253–257 (2023). 10.1587/transele.2022OMS0007 - DOI
-
- Revathi S., Padmanabhan R., “Design and development of piezoelectric composite-based micropump,” J. Microelectromech. Syst. 27(6), 1105–1113 (2018). 10.1109/JMEMS.2018.2870949 - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
