Drug Interactions of Imperatorin and Curcumin on Macitentan in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 40322036
- PMCID: PMC12049132
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S505960
Drug Interactions of Imperatorin and Curcumin on Macitentan in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to establish an in vitro incubation system and an in vivo model to investigate the potential kinetic interactions of macitentan with imperatorin and curcumin, and to validate the potential inhibitory mechanisms using molecular docking.
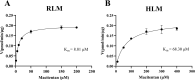
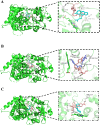
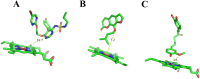
Methods: In vitro, the enzyme kinetic profile of macitentan was explored in rat liver microsomes (RLM) and human liver microsomes (HLM). Furthermore, molecular docking technique was used to study the sites of action of macitentan, imperatorin, and curcumin with CYP 3A4. In vivo, the pharmacokinetic parameters of macitentan were investigated in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats administered the drug orally, both as a single agent and in combination with imperatorin and curcumin.
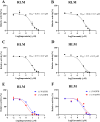
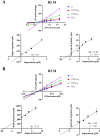
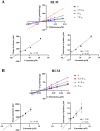
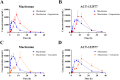
Results: In vitro, the results indicated that imperatorin and curcumin could inhibit the metabolism of macitentan, with IC50 values of 6.58 μM and 10.86 μM in RLM and 6.97 μM and 5.71 μM in HLM, respectively. And in the study of inhibition type, in RLM, the inhibition types of imperatorin and curcumin on macitentan were mixed and non-competitive, respectively; in HLM, the inhibition types of imperatorin and curcumin on macitentan were both mixed. Furthermore, additional molecular docking studies demonstrated that both imperatorin and curcumin occupied the CYP3A4 site. In vivo, the result showed significant increases in AUC(0-t), AUC(0-∞), Tmax, t1/2, and Cmax for macitentan while a decrease in CLz/F when combined with imperatorin. The metabolite ACT-132577 exhibited substantial increases in t1/2, Tmax, and Cmax. Combined with curcumin, the AUC(0-∞) and Tmax of macitentan were significantly increased, while CLz/F was significantly decreased. Conversely, the metabolite ACT-132577 exhibited a substantial decrease in CLz/F, accompanied by notable increases in AUC(0-∞) and Tmax.
Conclusion: In vitro and in vivo studies revealed that imperatorin and curcumin exhibited inhibitory effects on the metabolism of macitentan. Furthermore, molecular docking revealed that the metabolic inhibition of macitentan by imperatorin and curcumin occurred through binding to the site on CYP3A4. However, further investigation is necessary to ascertain whether this phenomenon will occur in humans.
Keywords: UPLC-MS/MS; inhibition mechanism; molecular docking; pharmacokinetics.
© 2025 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of imperatorin on dabrafenib metabolism in vitro and in vivo.Chem Biol Interact. 2024 Aug 25;399:111131. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111131. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Chem Biol Interact. 2024. PMID: 38964639
-
Development of UPLC-MS/MS method for studying the pharmacokinetic interactions of fuzuloparib with curcumin in rats.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024 Oct 15;249:116383. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2024.116383. Epub 2024 Jul 28. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2024. PMID: 39096626
-
Differential inhibition of sildenafil and macitentan on saxagliptin metabolism.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2024 May;486:116934. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2024.116934. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38663673
-
Inhibitory effects of nimodipine, nitrendipine and felodipine on tamoxifen metabolism and molecular docking.Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;236:116854. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.116854. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40054784
-
Effect of ponatinib on the metabolism of cariprazine in vitro and in vivo and the underlying mechanism.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;499:117353. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2025.117353. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40286877
Cited by
-
Advancing cancer therapy: Nanomaterial-based encapsulation strategies for enhanced delivery and efficacy of curcumin.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jun 9;33:101963. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101963. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40575656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

