The Changing Impact of Human Cytomegalovirus Serology and Infection on Patient Outcome After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Italian Prospective Multicenter Survey in the Era of Letermovir Prophylaxis
- PMID: 40322267
- PMCID: PMC12048776
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf233
The Changing Impact of Human Cytomegalovirus Serology and Infection on Patient Outcome After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Italian Prospective Multicenter Survey in the Era of Letermovir Prophylaxis
Abstract
Background: In the letermovir primary prophylaxis (LET-PP) era, the epidemiology of human cytomegalovirus infection (HCMV-i) in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HSCT) recipients has changed.
Methods: We prospectively evaluated incidence and risk factors for clinically significant (CS) HCMV-i at 180 days from transplant and 1-year overall survival in 1310 allo-HSCTs performed from January 2021 to March 2022 according to LET-PP use.
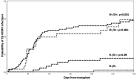
Results: The cumulative incidence of CS-HCMV-i at 100 and 180 days from transplant was 3.8% and 16%, respectively, in patients who received LET-PP, and 14% and 17% in patients who did not. Variables associated with increased risk of CS-HCMV-i in patients who received LET-PP included transplant from an HCMV-seronegative donor, transplant from a donor other than matched related, >20 days to engraftment, and acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Transplant in HCMV-seropositive recipients was associated with increased risk of CS-HCMV-i in patients who did not receive LET-PP. One-year overall survival after transplant was 81.1%. Acute leukemia, disease not in remission at transplant, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status >1, >20 days to engraftment, acute GVHD, CS Epstein-Barr virus DNAemia, gram-negative bacteremia, and invasive fungal disease were associated with increased mortality in patients who received LET-PP. HCMV recipient seropositivity, Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index score ≥3, and gram-negative bacteremia were associated with increased mortality in patients who did not receive LET-PP.
Conclusions: In patients who received LET-PP, recipient/donor serology no longer correlates with early CS-HCMV-i whereas it still predicts late CS-HCMV-i as well as risk of CS-HCMV-i in patients who did not receive LET-PP. Donor serology, CS-HCMV-i and HCMV disease no longer impact survival in allo-HSCT recipients who receive LET-PP. Clinical Trials Registration. NCT04412811.
Keywords: allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant; epidemiology; human cytomegalovirus; letermovir prophylaxis; survival.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures


References
-
- Ljungman P, de la Camara R, Robin C, et al. Guidelines for the management of cytomegalovirus infection in patients with haematological malignancies and after stem cell transplantation from the 2017 European Conference on Infections in Leukaemia (ECIL 7). Lancet Infect Dis 2019; 19:e260–72. - PubMed
-
- Girmenia C, Lazzarotto T, Bonifazi F, et al. Assessment and prevention of cytomegalovirus infection in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant and in solid organ transplant: a multidisciplinary consensus conference by the Italian GITMO, SITO, and AMCLI societies. Clin Transplant 2019; 33:e13666. - PubMed
-
- Nichols WG, Corey L, Gooley T, Davis C, Boeckh M. High risk of death due to bacterial and fungal infection among cytomegalovirus (CMV)-seronegative recipients of stem cell transplants from seropositive donors: evidence for indirect effects of primary CMV infection. J Infect Dis 2002; 185:273–82. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

