Potential of Fruits to Improve Dyslipidemias: A Pilot Review
- PMID: 40322293
- PMCID: PMC12050025
- DOI: 10.2147/VHRM.S488465
Potential of Fruits to Improve Dyslipidemias: A Pilot Review
Abstract
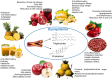
Dyslipidemia is a condition characterized by excessive lipids in the blood plasma, including triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and decreased levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), which is generated mostly due to obesity. This study aims to summarize research conducted on rats and humans regarding the potential of eight fruits in reducing dyslipidemia and their associated health benefits (eg, reduction of free radicals, hypoglycemic effects, weight reduction, lowering of blood pressure, and anti-inflammatory properties). The studied fruits include pomegranate, star fruit, Rosa roxburghii, pineapple, tree tomato, coffee, apple, and passion fruit. Various parts of these fruits, such as the root, leaves, stem, peel, and pulp, were analyzed for their effects. These fruits are edible, widely available, and cost-effective when purchased during the harvest season (Graphical abstract).
Keywords: benefits; dyslipidemias; fruits; humans; rats.
© 2025 Flores Flores et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures







References
-
- Isas AS, Escobar F, Álvarez-Villamil E, et al. Fermentation of pomegranate juice by lactic acid bacteria and its biological effect on mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Biosci. 2023;53:102516. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2023.102516 - DOI
-
- Halim NAA, Karim CF, Mohammed IK, et al. Anti-obesity effect of methanolic extracts of local punica granatum in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Malaysian J Med Health Sci. 2023;18(2):228–236. doi: 10.47836/MJMHS.19.2.33 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

