Prevalence and Outcome of Infections Caused by Staphylococcus aureus Strains Harboring the Panton-Valentine Leukocidin Gene
- PMID: 40322341
- PMCID: PMC12049733
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81687
Prevalence and Outcome of Infections Caused by Staphylococcus aureus Strains Harboring the Panton-Valentine Leukocidin Gene
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus, especially Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), is responsible for various hospital-acquired (HA) and community-acquired (CA) infections. Mec A gene responsible for methicillin resistance is encoded in Staphylococcal cassette chromosome gene (SCC). CA-MRSA strains often carry SCC mec IV / SCC mec V and Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) genes. PVL-producing MRSA can cause severe skin or soft tissue infections.
Aim: This study estimates the prevalence and outcome of infections caused by PVL-producing S. aureus strains in outdoor and indoor patients of a tertiary care hospital in Western Maharashtra, India.
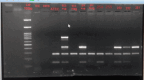
Method: This cross-sectional study included 274 S. aureus strains isolated from various clinical samples during the study period. Detection of Methicillin resistance was done by the cefoxitin disk method and by automated antimicrobial susceptibility (Vitek 2) method. Multiplex PCR was done for the detection of MecA, SCC type IV, Nuc, and PVL gene using appropriate primers.
Results: Out of 274 S. aureus strains, 151 (55%) were methicillin resistant. The PVL gene was detected in 187 (70.8%) strains and SCC IV in 116 (43.9%) strains. Mec A was detected in all MRSA strains. Both PVL-producing MRSA (83.4%) and MSSA (78.78) strains were isolated commonly from pus samples. Patients with PVL-producing S. aureus infections required more surgical interventions (18.1%) as compared to those with PVL-negative infections (5.19%) (p-value = 0.006). The PVL gene was associated with SCC IV in 84 (58.7%) strains, while 35 (24.4%) PVL-positive strains were not associated with SCC IV. Few SCC IV and PVL-positive S. aureus strains (17 strains) have produced HA infections.
Conclusion: The prevalence of the PVL gene is 70.8% in S. aureus. PVL and SCC IV genes are markers of CA infection. MRSA strains harbouring PVL and SCC IV gene producing HA infections is a cause of concern. This suggests infiltration of SCC IV gene producing S. aureus strains in hospital settings. Proper antibiotic stewardship practices, strict aseptic techniques, identification, and treatment of carriers are needed to control the spread of CA-MRSA in hospitals and in the community.
Keywords: community-acquired methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (ca-mrsa); hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (ha-mrsa); methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus; pvl gene; scc iv gene.
Copyright © 2025, Thakar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Bharati Vidyapeeth (Deemed to be University) Medical College Institutional Ethics Committee issued approval BVDUMC/IEC/19, dated 25/04/2022. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


References
-
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: related infections and antibiotic resistance. Stefani S, Goglio A. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14 Suppl 4:0–22. - PubMed
-
- Identification of scc mec methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from hospitals’ clinical samples in Jambi using polymerase chain reaction (pcr) Humaryanto H, Lipinwati L, Hanina H, Simanjuntak C. Indo J of Trop and Infect Dis. 2020;8:77–82.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
