Successful Treatment of Unscheduled Uterine Bleeding During Transdermal Menopausal Hormone Therapy Combined With Bazedoxifene
- PMID: 40322348
- PMCID: PMC12045705
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81582
Successful Treatment of Unscheduled Uterine Bleeding During Transdermal Menopausal Hormone Therapy Combined With Bazedoxifene
Abstract
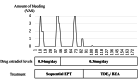
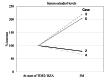
Abnormal uterine bleeding and withdrawal bleeding are noted as crucial causal factors for dropout of postmenopausal women during menopausal hormone therapy (MHT). We report the potential for treatment of unscheduled uterine bleeding during transdermal MHT by switching to transdermal 17-beta estradiol (TDE2) and bazedoxifene acetate (BZA) (TDE2/BZA) and evaluate the side effects of this treatment on the recurrence of climacteric symptoms in the five reported patients. Five postmenopausal women were treated with estrogen-progestin therapy (EPT) which included TDE2 and progestin formulation for MHT. The progestin formulation was replaced with BZA, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, due to unscheduled uterine bleeding. Four of five postmenopausal women were evaluated in terms of estrogen dynamics and recurrence of climacteric symptoms. In all cases examined in this report, unscheduled uterine bleeding resolved within one month. In two of four patients in whom climacteric symptoms recurred, their serum estradiol levels were surprisingly elevated three months after the start of TDE2/BZA. This is the first report, to our knowledge, of the successful treatment of unscheduled uterine bleeding by TDE2/BZA during MHT and a suggested correlation between estrogen dynamics and concomitant recurrence of side effects caused by TDE2/BZA.
Keywords: abnormal uterine bleeding; bazedoxifene; menopausal hormone therapy; tissue-selective estrogen complex; transdermal 17-beta estradiol.
Copyright © 2025, Koike et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Effect of age on reasons for initiation and discontinuation of hormone replacement therapy. Ettinger B, Pressman A, Silver P. Menopause. 1999;6:282–289. - PubMed
-
- Conjugated estrogens/bazedoxifene (Duavee): a novel agent for the treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause and the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Goldberg T, Fidler B. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4357350/ P T. 2015;40:178–182. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tissue-selective estrogen complex for women who experience breast discomfort or vaginal bleeding when on hormone therapy. Kim SE, Lee DY, Choi D. Menopause. 2019;26:383–386. - PubMed
-
- Tissue-selective estrogen complex for menopausal hormone therapy. Pinkerton JV. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2018;61:463–469. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
