Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- PMID: 40322465
- PMCID: PMC12048903
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2025-1182
Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Paclitaxel (PTX) chemotherapy frequently induces cognitive impairment, which is closely associated with two key pathological processes: necroptosis of hippocampal neurons and microglial polarization. Necroptotic neurons release damage-associated molecular patterns, triggering inflammatory responses. As the primary immune cells in the central nervous system, microglia can exhibit either pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory activity depending on their polarization state. However, the relationship between PTX-induced neuronal necroptosis and microglial activation remains unclear.
Methods: In this study, both in vivo and in vitro experiments were conducted. In vivo, an adult male C57BL/6N mouse model of PTX-induced cognitive impairment was established and divided into three groups: Veh (vehicle control), PTX (paclitaxel only), and P + N (paclitaxel with Nec-1 treatment). Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1), a specific inhibitor of RIPK1, was used to inhibit necroptosis. In vitro, HT22 cells were used to prepare necroptosis-conditioned medium, and BV-2 cells were treated with this medium. TAK-242, a TLR4 inhibitor, was used to explore the role of the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway. Immunofluorescence staining, western blot, and ELISA were employed to detect relevant markers and cytokines.
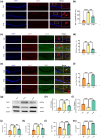
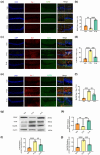
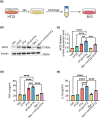
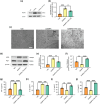
Results: The results demonstrated that PTX-induced necroptosis of hippocampal neurons activated microglia. Nec-1 effectively suppressed neuronal necroptosis and reduced M1 polarization of microglia. The TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway was involved in microglial polarization induced by the necroptotic-conditioned medium of PTX-treated HT22 cells. TAK-242 significantly blocked the regulatory effect of PTX-induced neuronal necroptosis on BV-2 microglial polarization.
Conclusion: This study reveals that hippocampal neuron necroptosis activates microglia through the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in PTX-induced cognitive impairment, promoting M1 polarization and neuroinflammation. Inhibiting necroptosis promotes M2 polarization and neuroprotection. These findings uncover a novel mechanism of PTX-induced cognitive impairment and suggest potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: DAMPs; TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway; microglia polarization; necroptosis; paclitaxel.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spinal microglial M1 polarization contributes paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain by triggering cells necroptosis.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024 Mar;38(3):e23669. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23669. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38459698
-
Paclitaxel induces cognitive impairment via necroptosis, decreased synaptic plasticity and M1 polarisation of microglia.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1556-1565. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2108064. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35944285 Free PMC article.
-
Free heme induces neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment by microglial activation via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 5;22(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01387-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38183122 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol Improves Paclitaxel-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Mice by Activating SIRT1/PGC-1α Pathway to Regulate Neuronal State and Microglia Cell Polarization.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Apr 12;17:1125-1138. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S400936. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37077409 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative analgesia with morphine promoting microglial activation and neuroinflammation induced by surgery aggravates perioperative neurocognitive dysfunction in aged mice.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Dec 17;18:39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.12.008. eCollection 2025 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39816480 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hermelink K. Acute and late onset cognitive dysfunction associated with chemotherapy in women with breast cancer. Cancer. 2011 Mar;117(5):1103–4. - PubMed
-
- Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Vanden Berghe T, Kroemer G. Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: an ordered cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;11(10):700–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
