APOBEC3 Activity Promotes the Survival and Evolution of Drug-Tolerant Persister Cells during EGFR Inhibitor Resistance in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 40323013
- PMCID: PMC12093302
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0442
APOBEC3 Activity Promotes the Survival and Evolution of Drug-Tolerant Persister Cells during EGFR Inhibitor Resistance in Lung Cancer
Abstract
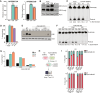
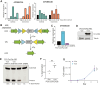
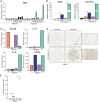
APOBEC mutagenesis is one of the most common endogenous sources of mutations in human cancer and is a major source of genetic intratumor heterogeneity. High levels of APOBEC mutagenesis are associated with poor prognosis and aggressive disease across diverse cancers, but the mechanistic and functional impacts of APOBEC mutagenesis on tumor evolution and therapy resistance remain relatively unexplored. To address this, we investigated the contribution of APOBEC mutagenesis to acquired therapy resistance in a model of EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. We find that inhibition of EGFR in lung cancer cells leads to a rapid and pronounced induction of APOBEC3 expression and activity. Functionally, APOBEC expression promotes the survival of drug-tolerant persister cells (DTP) following EGFR inhibition. Constitutive expression of APOBEC3B alters the evolutionary trajectory of acquired resistance to the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib, making it more likely that resistance arises through de novo acquisition of the T790M gatekeeper mutation and squamous transdifferentiation during the DTP state. APOBEC3B expression is associated with increased expression of the squamous cell transcription factor ΔNp63 and squamous cell transdifferentiation in gefitinib-resistant cells. Knockout of p63 in gefitinib-resistant cells reduces the expression of the ΔNp63 target genes IL-1α/β and sensitizes these cells to the third-generation EGFR inhibitor osimertinib. These results suggest that APOBEC activity promotes acquired resistance by facilitating evolution and transdifferentiation in DTPs and that approaches to target ΔNp63 in gefitinib-resistant lung cancers may have therapeutic benefit.
Significance: APOBEC mutagenesis is a common source of genetic heterogeneity in cancer, and APOBEC mutational signatures are enriched in metastatic and drug-resistant tumors. However, the mechanisms through which APOBEC3 enzymes promote tumor evolution remain unknown. In this study, we show that APOBEC3 activity contributes to the development of therapy-resistant cancer cells by promoting evolution of DTP cells. These findings offer insights into the role of APOBEC mutagenesis in cancer progression.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
N.M.G. Garcia reports grants from Howard Hughes Medical Institute Gilliam Fellowship during the conduct of the study. A.V. DiMarco reports grants from NCI and NIH during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from Genentech and Merck outside the submitted work. J.V. Alvarez reports grants from NCI during the conduct of the study. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures



Update of
-
APOBEC3 activity promotes the survival and evolution of drug-tolerant persister cells during acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 20:2023.07.02.547443. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.02.547443. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cancer Res Commun. 2025 May 1;5(5):825-840. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0442. PMID: 37461590 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Jamal-Hanjani M, Wilson GA, McGranahan N, Birkbak NJ, Watkins TBK, Veeriah S, et al. Tracking the evolution of non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2017;376:2109–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

