Tracking inflammation status for improving patient prognosis: A review of current methods, unmet clinical needs and opportunities
- PMID: 40324661
- PMCID: PMC12173025
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2025.108592
Tracking inflammation status for improving patient prognosis: A review of current methods, unmet clinical needs and opportunities
Abstract
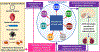
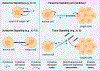
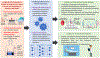
Inflammation is the body's response to infection, trauma or injury and is activated in a coordinated fashion to ensure the restoration of tissue homeostasis and healthy physiology. This process requires communication between stromal cells resident to the tissue compartment and infiltrating immune cells which is dysregulated in disease. Clinical innovations in patient diagnosis and stratification include measures of inflammatory activation that support the assessment of patient prognosis and response to therapy. We propose that (i) the recent advances in fast, dynamic monitoring of inflammatory markers (e.g., cytokines) and (ii) data-dependent theoretical and computational modeling of inflammatory marker dynamics will enable the quantification of the inflammatory response, identification of optimal, disease-specific biomarkers and the design of personalized interventions to improve patient outcomes - multidisciplinary efforts in which biomedical engineers may potentially contribute. To illustrate these ideas, we describe the actions of cytokines, acute phase proteins and hormones in the inflammatory response and discuss their role in local wounds, COVID-19, cancer, autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative diseases and aging, with a central focus on cardiac surgery. We also discuss the challenges and opportunities involved in tracking and modulating inflammation in clinical settings.
Keywords: Acute phase proteins; Cytokines; Data-driven modeling; Health prognostics; Hormones; Inflammatory biomarkers; Wearable health monitoring.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Ralph Weissleder has consulted for ModeRNA, Boston Scientific, Lumicell, Seer Biosciences, Earli, and Accure Health, none of whom contributed or were involved in this research. Anthony Guiseppi Elie is the founder, president, and scientific director of ABTECH Scientific, Inc., a manufacturer of microfabricated electrodes, devices and systems used in biomedical diagnostics and the measurement of physiological biomarker status. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the findings. Simon A. Jones has received funding support from Hoffman-La Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Mestag Therapeutics and NovImmune SA and has acted as an advisory consultant for Roche, Chugai Pharmaceuticals, NovImmune SA, MAb Designs, Genentech, Sanofi Regeneron, Johnson & Johnson, Janssen Pharmaceuticals and Eleven Biotherapeutics. The other authors do not declare any competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abbate A, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Brugaletta S, Liuzzo G, Biasucci LM, 2003. C-reactive protein and other inflammatory biomarkers as predictors of outcome following acute coronary syndromes. In: Seminars in Vasc. Med, vol. 10001 Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc., 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY, pp. 375–384. Copyright© 2003 by. - PubMed
-
- Acharya M, Dunning J, 2010. Does the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs after cardiac surgery increase the risk of renal failure? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg 11, 461–467. - PubMed
-
- Aggas JR, Abasi S, Ton C, Salehi S, Liu R, Brandacher G, Grayson WL, Guiseppi-Elie A, 2023. Real-time monitoring using multiplexed multi-electrode bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy for the stratification of vascularized composite allografts: a perspective on predictive analytics. Bioeng 10, 434. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

