Aquatic insects as mediator for microplastics pollution in a river ecosystem of Bangladesh
- PMID: 40325097
- PMCID: PMC12053624
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-88024-1
Aquatic insects as mediator for microplastics pollution in a river ecosystem of Bangladesh
Abstract
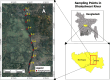
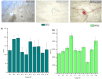
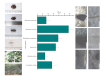
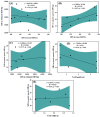
Microplastics (MPs) are emerging pollutants that threaten the aquatic ecosystem. Aquatic insects may play a crucial role in moving MPs into different trophic levels within and across the ecosystems. However, field-level evidence is still insufficient globally despite its tremendous ecological significance. Thus, for the first time in Bangladesh, MPs were explored in six species of aquatic insects along with water and sediment of the Daleshwari River. Digestion and density separation methods were used for the extraction of MPs. Microscopic inspection and Fourier transform spectroscopy (FT-IR) were done to identify and quantify MPs. The average concentration of MPs in sediment and water is 143.1 ± 28.52 of MPs/L and 30153.8 ± 2313.62 of MPs/kg, respectively. In aquatic species, the highest MPs found in D. rusticus (57.82 ± 14.98 MPs/g), followed by B. contaminate (38.53 ± 6.87 MPs/g), Ranatra sp. (34.05 ± 5.39 MPs/g), C. servilia (26.99 ± 7.88 MPs/g), D. annulatus (16.44 ± 6.95 MPs/g), and O. sabina (14.13 ± 4.52 MPs/g). A total of eight types of polymers have been identified. It was important to notice that the studied aquatic insects bear similar MPs (size, shape, and color) found in water and sediments from the river. It reveals the potential for the insects (accumulators of MPs) to be a driving factor for the transport of the MPs across different ecosystems. It has also been found that Aquatic insect's size, weight, feeding habitat, and host reserviour could be responsible for MPs ingestion. In addition, ecological risk assessment (Contamination Factor, Nemerrow Pollution Index, Pollution Load Index, Polymer Hazard Index) indicates different levels of risk for the pertaining river ecosystem.
Keywords: Aquatic insects; Bioaccumulation factor (BAF); Microplastics (MPs); Pollution Hazard Index (PHI); Pollution load index (PLI).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Shahnewaz, H. M., Hasan, J., Manik, M. & Ahmed, M. Pervasiveness of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of some selected fi sh species from Turag River alongside the capital city of Bangladesh. Emerg. Contam.10, 100309 (2024). - DOI
-
- Haque, M. R. et al. Assessment of microplastics pollution in aquatic species (fish, crab, and snail), water, and sediment from the Buriganga River, Bangladesh: An ecological risk appraisals. Sci. Total Environ.857 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Plastics Europe. Plastics – the fast facts 2023. Plastics Europe (2023). https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-fast-facts-2023/
-
- Sharma, S., Bhardwaj, A., Thakur, M. & Saini, A. Understanding Microplastic Pollution of Marine Ecosystem: A Review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research (Springer, 2023). 10.1007/s11356-023-28314-1 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

