Functional mitochondrial respiration is essential for glioblastoma tumour growth
- PMID: 40325182
- PMCID: PMC12277175
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-025-03429-6
Functional mitochondrial respiration is essential for glioblastoma tumour growth
Erratum in
-
Correction: Functional mitochondrial respiration is essential for glioblastoma tumour growth.Oncogene. 2025 Aug;44(30):2675. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03451-8. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 40468053 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
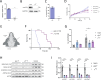
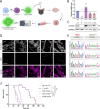
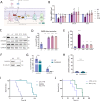
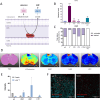
Horizontal transfer of mitochondria from the tumour microenvironment to cancer cells to support proliferation and enhance tumour progression has been shown for various types of cancer in recent years. Glioblastoma, the most aggressive adult brain tumour, has proven to be no exception when it comes to dynamic intercellular mitochondrial movement, as shown in this study using an orthotopic tumour model of respiration-deficient glioblastoma cells. Although confirmed mitochondrial transfer was shown to facilitate tumour progression in glioblastoma, we decided to investigate whether the related electron transport chain recovery is necessary for tumour formation in the brain. Based on experiments using time-resolved analysis of tumour formation by glioblastoma cells depleted of their mitochondrial DNA, we conclude that functional mitochondrial respiration is essential for glioblastoma growth in vivo, because it is needed to support coenzyme Q redox cycling for de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis controlled by respiration-linked dihydroorotate dehydrogenase enzyme activity. We also demonstrate here that astrocytes are key mitochondrial donors in this model.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Vargas JNS, Hamasaki M, Kawabata T, Youle RJ, Yoshimori T. The mechanisms and roles of selective autophagy in mammals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24:167–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

