TWEAK regulates the functions of hair follicle stem cells via the Fn14-Wnt/β-catenin-CXCR4 signalling axis
- PMID: 40325995
- PMCID: PMC12053109
- DOI: 10.1111/wrr.70032
TWEAK regulates the functions of hair follicle stem cells via the Fn14-Wnt/β-catenin-CXCR4 signalling axis
Abstract
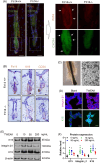
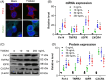
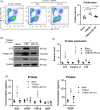
Hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs) are crucial for maintaining cutaneous functions under various pathological conditions, including wounds. Tumour necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) interacts with its receptor, fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (Fn14), and plays a role in the development and tissue repair of skin diseases. This study aims to elucidate the effects of TWEAK/Fn14 signalling on HFSCs and the associated mechanisms. The expressions of HFSC markers, including K19, integrin β1 and K15, were analysed via immunohistochemistry in normal and Fn14-deficient mouse skin. Primary HFSCs were cultured in vitro and then treated with TWEAK or a chemokine (CXC motif) (CXCR) 4 inhibitor. The phenotype markers and secreted cytokines of HFSCs were assessed via immunofluorescence analysis, Western blotting and real-time polymerase chain reaction. Our results showed that both Fn14 and CXCR4 were highly expressed in hair follicles. Fn14 deficiency led to a decrease in the expression levels of K19 and CD34. Exogenous TWEAK enhanced the expression of K15, K19, integrin β1, tumour necrosis factor receptor type 2 and CXCR4 in cultured HFSCs. Additionally, TWEAK induced the proliferation, migration and cytokine production in HFSCs. Furthermore, the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway was upregulated in HFSCs upon TWEAK stimulation, and inhibitors of β-catenin or CXCR4 suppressed the effects of TWEAK on the differentiation and secretory functions of HFSCs. In conclusion, TWEAK/Fn14 interaction regulates the expression of differentiation markers and secretory functions of HFSCs in vitro. Wnt/β-catenin signalling or CXCR4 activation mediates the effects of TWEAK on HFSCs. Targeting the Fn14-Wnt/β-catenin-CXCR4 signalling axis may offer a potential approach for managing HFSC-related skin diseases, such as wounds.
Keywords: CXCR4; Fn14; TNFR; TWEAK; hair follicle stem cell.
© 2025 The Author(s). Wound Repair and Regeneration published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Wound Healing Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dahuang-Gancao decoction ameliorates testosterone-induced androgenetic alopecia in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Feb 11;341:119347. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119347. Epub 2025 Jan 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39800247
-
Exosome-derived long non-coding RNA AC010789.1 modified by FTO and hnRNPA2B1 accelerates growth of hair follicle stem cells against androgen alopecia by activating S100A8/Wnt/β-catenin signalling.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Jan;15(1):e70152. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70152. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39748192 Free PMC article.
-
TWEAK/Fn14 interaction induces proliferation and migration in human airway smooth muscle cells via activating the NF-κB pathway.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Apr;119(4):3528-3536. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26525. Epub 2018 Jan 11. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29143982
-
TWEAK/Fn14 Activation Participates in Skin Inflammation.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:6746870. doi: 10.1155/2017/6746870. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29038621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Mediates Fibroblast Growth Factor-Inducible 14 Signaling.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(2):579-588. doi: 10.1159/000480530. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28934756 Review.
References
-
- Ibrahim MR, Medhat W, El‐Fakahany H, Abdel‐Raouf H, Snyder EY. The developmental & molecular requirements for ensuring that human pluripotent stem cell‐derived hair follicle bulge stem cells have acquired competence for hair follicle generation following transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2021;30:9636897211014820. doi:10.1177/09636897211014820 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 24YXYJ0001/Key Medical Research Plan of Xi'an City
- Special Support Program for High-Level Talents of Shaanxi Province
- 2024JC-YBQN-0810/Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province
- 2023SFYZ003/Research Grant of Maternal and Child Health Hospital of Hubei Province
- 2024TD-15/Innovation Capability Support Plan of Shaanxi Health Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

