What is chronic urinary tract infection? A systematic review
- PMID: 40326061
- PMCID: PMC12134415
- DOI: 10.1111/bju.16764
What is chronic urinary tract infection? A systematic review
Abstract
Objective: To define 'chronic' urinary tract infection (UTI) by reviewing current published research that employs this term.
Methods: We systematically searched Medline and Embase for studies covering all aspects of human UTI. For comparison, current urological and infectious disease guidelines were also reviewed.
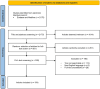
Results: The electronic search yielded a total of 2175 articles, of which 154 were eventually included for data extraction. Of these, six studies presented a definition of chronic UTI within the text. The definitions were highly incongruent among studies and often identical to the current definition of 'recurrent' UTI.
Conclusion: Chronic UTI is an undefined term, which has nevertheless been increasingly used in the past 15 years. Chronic UTI does not represent a distinct clinical or microbiological condition that justifies its use as medical diagnosis.
Keywords: bladder infection; chronic urinary tract infection; disease definition; recalcitrant urinary tract infection; recurrent urinary tract infection; unresolved urinary tract infection; urinary tract infection; urological guidelines.
© 2025 The Author(s). BJU International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of BJU International.
Figures

References
-
- Foxman B. Urinary tract infection syndromes: occurrence, recurrence, bacteriology, risk factors, and disease burden. Infect Dis Clin N Am 2014; 28: 1–13 - PubMed
-
- Anger J, Lee U, Ackerman AL et al. Recurrent uncomplicated urinary tract infections in women: AUA/CUA/SUFU guideline. J Urol 2019; 202: 282–289 - PubMed
-
- Aydin A, Ahmed K, Zaman I, Khan MS, Dasgupta P. Recurrent urinary tract infections in women. Int Urogynecol J 2015; 26: 795–804 - PubMed
-
- The Guideline Uroweb. https://uroweb.org/guidelines/urological‐infections/chapter/the‐guideline
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

