Cancer-Specific RNA Modifications in Tumour-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Tumour Growth
- PMID: 40326665
- PMCID: PMC12053886
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.70083
Cancer-Specific RNA Modifications in Tumour-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Tumour Growth
Abstract
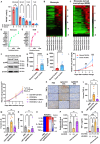
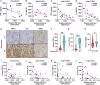
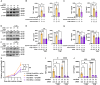
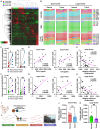
RNA modifications are crucial in cellular processes, and their dysregulation is linked to diseases like cancer. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) contain various RNAs and might be susceptible to modifications, but detecting these modifications has been challenging due to the small amount of RNA in EVs. We successfully detected 22 RNA modifications in EVs using a proprietary ultra-HPLC MS/MS system. We identified reduced levels of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in EVs derived from colon cancer tissues, which correlated with cancer recurrence. Increasing m6A levels via m6A demethylase Alkbh5 knockout suppressed the tumour-promoting effects of colorectal cancer EVs. Mechanistically, colorectal cancer-derived EVs increased tumour necrotic factor α and interleukin-6 secretion by macrophages via Toll-like receptor 8 in an m6A-dependent manner, promoting cancer cell proliferation. RNA-sequencing analysis showed that the levels of 5'-half-tRNA fragment (5'-half)-GlyGCC as well as those of m6A-modified 5'-half-GlyGCC were higher and lower, respectively, in colorectal cancer EVs than in normal colon tissue EVs. Cancer-derived EVs containing 5'-half-GlyGCC significantly promoted tumour growth, which was impeded by macrophage depletion. These findings provide evidence that cancer-specific RNA modifications are present in EVs, promoting tumour progression by regulating immune cells.
Keywords: 5′‐half‐GlyGCC; RNA modification; colorectal cancer; extracellular vesicles; inflammatory cytokines.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

