RAG suppresses group 2 innate lymphoid cells
- PMID: 40326866
- PMCID: PMC12055012
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.98287
RAG suppresses group 2 innate lymphoid cells
Abstract
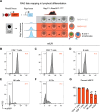
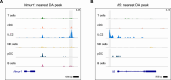
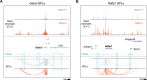
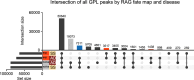
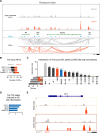
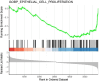
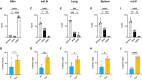
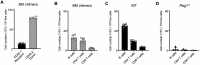
Antigen specificity is the central trait distinguishing adaptive from innate immune function. Assembly of antigen-specific T cell and B cell receptors occurs through V(D)J recombination mediated by the Recombinase Activating Gene endonucleases RAG1 and RAG2 (collectively called RAG). In the absence of RAG, mature T and B cells do not develop and thus RAG is critically associated with adaptive immune function. In addition to adaptive T helper 2 (Th2) cells, group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) contribute to type 2 immune responses by producing cytokines like Interleukin-5 (IL-5) and IL-13. Although it has been reported that RAG expression modulates the function of innate natural killer (NK) cells, whether other innate immune cells such as ILC2s are affected by RAG remains unclear. We find that in RAG-deficient mice, ILC2 populations expand and produce increased IL-5 and IL-13 at steady state and contribute to increased inflammation in atopic dermatitis (AD)-like disease. Furthermore, we show that RAG modulates ILC2 function in a cell-intrinsic manner independent of the absence or presence of adaptive T and B lymphocytes. Lastly, employing multiomic single cell analyses of RAG1 lineage-traced cells, we identify key transcriptional and epigenomic ILC2 functional programs that are suppressed by a history of RAG expression. Collectively, our data reveal a novel role for RAG in modulating innate type 2 immunity through suppression of ILC2s.
Keywords: RAG; allergic; atopic; dermatitis; immunology; inflammation; innate lymphoid cell; mouse.
© 2024, Ver Heul et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AV has contributed to scientific advisory boards at Galderma, Novartis, and Sanofi-Regeneron and has performed sponsored research for Amgen and Celldex, MM is affiliated with Sanofi, LZ, MT, TY, AT, DK, HJ, SV, CH, JK, JS No competing interests declared, BK Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures
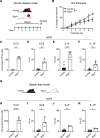
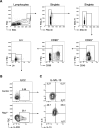
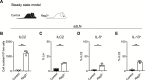


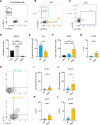








Update of
-
RAG suppresses group 2 innate lymphoid cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 20:2024.04.23.590767. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.23.590767. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Elife. 2025 May 06;13:RP98287. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98287. PMID: 38712036 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
RAG suppresses group 2 innate lymphoid cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 20:2024.04.23.590767. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.23.590767. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Elife. 2025 May 06;13:RP98287. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98287. PMID: 38712036 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
PGI2 restricts trained ILC2 responses in allergic inflammation.J Immunol. 2025 Jul 1;214(7):1582-1591. doi: 10.1093/jimmun/vkaf088. J Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40334085
-
Blocking CD226 regulates type 2 innate lymphoid cell effector function and alleviates airway hyperreactivity.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 May;153(5):1406-1422.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2024.01.003. Epub 2024 Jan 19. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38244725
-
Interactions Between the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1476:297-308. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-85340-1_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40622548 Review.
-
Disease pathogenesis and barrier functions regulated by group 3 innate lymphoid cells.Semin Immunopathol. 2024 Jan;45(4-6):509-519. doi: 10.1007/s00281-024-01000-1. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Semin Immunopathol. 2024. PMID: 38305897 Review.
References
-
- Altin JA, Daley SR, Howitt J, Rickards HJ, Batkin AK, Horikawa K, Prasad SJ, Nelms KA, Kumar S, Wu LC, Tan SS, Cook MC, Goodnow CC. Ndfip1 mediates peripheral tolerance to self and exogenous antigen by inducing cell cycle exit in responding CD4+ T cells. PNAS. 2014;111:2067–2074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1322739111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 AR077007/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR070116/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI167047/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR080219/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007163/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI167047/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI167933/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AI154912/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- AR070116/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI154912/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- AR077007/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI167933/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- AR080219/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- International Scholarship/Japanese Society of Allergology
- AI007163/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

