Coordinated Transcriptional Increases in Cell Wall Synthesis Genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae Lacking the Lytic Transglycosylase, ltgA
- PMID: 40327097
- PMCID: PMC12055626
- DOI: 10.1007/s00284-025-04261-7
Coordinated Transcriptional Increases in Cell Wall Synthesis Genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae Lacking the Lytic Transglycosylase, ltgA
Abstract
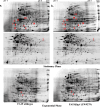
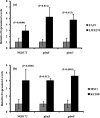
Lytic transglycosylase A in Neisseria gonorrhoeae cleaves the β-1,4-glycosidic bond between peptidoglycan (PG) monomers to liberate 1,6-anhydro-PG fragments that are either recycled or released as cytotoxic fragments. To gain further insight into the effect of LtgA on cellular processes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae, we performed a proteomic analysis comparing wild-type and an isogenic ltgA null mutant strain. Proteins were separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, which revealed several proteins that were increased in their level of expression upon loss of LtgA. The most notable changes corresponded to enzymes related to aminosugar and pyrimidine metabolism. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR of mRNA from a ltgA null strain confirmed increased transcription of genes encoding enzymes involved in UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) synthesis, a major precursor in PG and lipooligosaccharide (LOS) synthesis, during normal growth conditions and following exposure to penicillin. We also found that the ltgA mutant strains were more susceptible to β-lactam antibiotics, vancomycin, and the human-cathelicidin antibacterial peptide, LL-37, than their corresponding wild-type parental strains. Our results suggest that increased expression of enzymes responsible for production UDP-GlcNAc is an adaptive response due to inactivation of ltgA and/or exposure to penicillin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflicts of interests: The authors declare there are not conflicts of interests in these areas. Ethical Approval: Not applicable. Consent to Participate: Not required. Consent to Publications: Not required.
Figures






References
-
- Azariah S, Perkins N (2007) Risk factors and characteristics of patients with gonorrhoea presenting to Auckland sexual health service, New Zealand. N Z Med J 120(1252):U2491 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

