Incidence of major adverse kidney events after ICU admission in COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 ARDS patients
- PMID: 40328653
- PMCID: PMC12056615
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-094887
Incidence of major adverse kidney events after ICU admission in COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 ARDS patients
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the incidence and drivers of major adverse kidney events (MAKEs) between COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) patients, with a focus on long-term kidney outcomes.
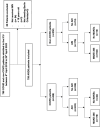
Design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Single-centre intensive care unit in the Midlands, UK.
Participants: 708 ARDS patients (458 COVID-19, 250 non-COVID-19).
Primary and secondary outcome measures: The primary outcome was MAKE at 365 days (MAKE-365), defined as new renal replacement therapy (RRT), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <75% of baseline or all-cause mortality. Secondary analyses examined non-mortality MAKE components.
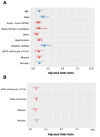
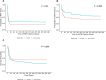
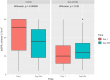
Results: The incidence of MAKE-365 was significantly higher in the non-COVID-19 group compared with the COVID-19 group (66% vs 39%, p<0.001), primarily driven by increased RRT initiation, followed by mortality and eGFR decline (p=0.055). Independent predictors of MAKE-365 included lower eGFR and elevated bilirubin in both groups. Age (p<0.001) and diabetes (p=0.041) were additional predictors in the COVID-19 cohort, while lower albumin (p=0.002) was significant in the non-COVID-19 group. Excluding mortality, RRT and eGFR decline remained significant drivers of MAKE outcomes in the non-COVID-19 cohort.
Conclusions: Non-COVID-19 ARDS patients face a greater risk of MAKE-365 and adverse kidney outcomes due to higher RRT requirements and mortality rates. These findings underscore the importance of tailored interventions and long-term nephrology follow-up, particularly for patients with reduced eGFR, elevated bilirubin and comorbidities like diabetes and hypoalbuminaemia.
Keywords: Acute renal failure; COVID-19; INTENSIVE & CRITICAL CARE; Intensive Care Units; Respiratory Distress Syndrome.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Alenezi FK, Almeshari MA, Mahida R, et al. Incidence and risk factors of acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients with and without acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) during the first wave of COVID-19: a systematic review and Meta-Analysis. Ren Fail. 2021;43:1621–33. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.2011747. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
