The efficacy and safety of rituximab monotherapy in the new onset pediatric idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: a randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 40328661
- PMCID: PMC12057790
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2499902
The efficacy and safety of rituximab monotherapy in the new onset pediatric idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: a randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Nephrotic syndrome (NS) is a common form of glomerular disease in children, characterized by a high propensity for relapse. Prolonged use of glucocorticoids (GCs) can result in various side effects. Rituximab (RTX) may be considered as an initial treatment option for primary nephrotic syndrome in pediatric patients.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, single-center, randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate whether the initial use of RTX monotherapy is superior to GC therapy in treating pediatric idiopathic NS and to assess its safety. The primary outcome and secondary outcomes were compared between the two groups.
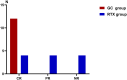
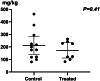
Results: A total of 24 pediatric patients were included in the study, comprising 19 males and 5 females. After six weeks of treatment, the complete remission (CR) rate in the GC group was significantly higher than that in the RTX group (100% vs 33.3%). Compared with the RTX group, the GC group had a shorter time to first remission (14.25 d vs. 9.5 d). During the follow-up period, none of the patients in the RTX group who achieved CR experienced relapse, with the longest relapse-free duration being 79 weeks. In the GC group, nine patients experienced relapse with the longest relapse-free period being 94 weeks. No serious adverse events occurred in either group. The cumulative steroid dosage was not statistically different between the 2 groups (p = 0.41).
Conclusion: Although the CR rate of children with idiopathic NS treated with RTX alone is significantly lower, the relapse rate among responders to RTX is also lower than that of the GC treatment.
Keywords: CD20 monoclonal antibody; Nephrotic syndrome; children; glucocorticoids; outcome; rituximab.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous