Impaired ketogenesis in Leydig Cells drives testicular aging
- PMID: 40328805
- PMCID: PMC12056170
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59591-8
Impaired ketogenesis in Leydig Cells drives testicular aging
Abstract
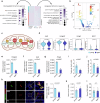
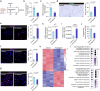
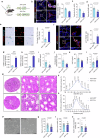
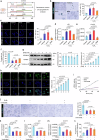
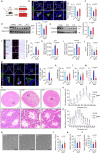
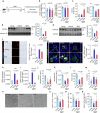
Testicular aging commonly leads to testosterone deficiency and impaired spermatogenesis, yet the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Here, we show that Leydig cells are particularly vulnerable to aging processes in testis. Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies the expression of Hmgcs2, the gene encoding rate-limiting enzyme of ketogenesis, decreases significantly in Leydig cells from aged mice. Additionally, the concentrations of ketone bodies β-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid in young testes are substantially higher than that in serum, but significantly diminish in aged testes. Silencing of Hmgcs2 in young Leydig cells drives cell senescence and accelerated testicular aging. Mechanistically, β-hydroxybutyric acid upregulates the expression of Foxo3a by facilitating histone acetylation, thereby mitigating Leydig cells senescence and promoting testosterone production. Consistently, enhanced ketogenesis by genetic manipulation or oral β-hydroxybutyric acid supplementation alleviates Leydig cells senescence and ameliorates testicular aging in aged mice. These findings highlight defective ketogenesis as a pivotal factor in testicular aging, suggesting potential therapeutic avenues for addressing age-related testicular dysfunction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Basaria, S. Reproductive aging in men. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am.42, 255–270 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Paul, C. & Robaire, B. Ageing of the male germ line. Nat. Rev. Urol.10, 227–234 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Juul, A. & Skakkebaek, N. E. Androgens and the ageing male. Hum. Reprod. Update8, 423–433 (2002). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

