Immunotherapy in lung cancer brain metastases
- PMID: 40328894
- PMCID: PMC12056043
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-025-00901-0
Immunotherapy in lung cancer brain metastases
Abstract
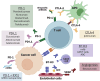
Brain metastases (BM) occur frequently in lung cancer, particularly in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and remain a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. Standard therapies have limited efficacy due to poor crossing of the blood-brain barrier and the distinct features between BM and the primary tumor. This review explores the immune landscape of brain metastatic disease, emerging immunotherapeutic strategies, and promising biomarkers in NSCLC patients.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

