Immune-epithelial-stromal networks define the cellular ecosystem of the small intestine in celiac disease
- PMID: 40328997
- PMCID: PMC12133578
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-025-02146-2
Immune-epithelial-stromal networks define the cellular ecosystem of the small intestine in celiac disease
Abstract
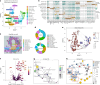
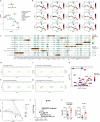
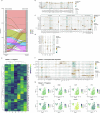
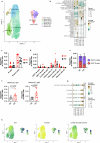
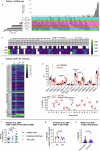
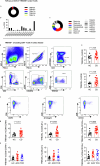
The immune-epithelial-stromal interactions underpinning intestinal damage in celiac disease (CD) are incompletely understood. To address this, we performed single-cell transcriptomics (RNA sequencing; 86,442 immune, parenchymal and epithelial cells; 35 participants) and spatial transcriptomics (20 participants) on CD intestinal biopsy samples. Here we show that in CD, epithelial populations shifted toward a progenitor state, with interferon-driven transcriptional responses, and perturbation of secretory and enteroendocrine populations. Mucosal T cells showed numeric and functional changes in regulatory and follicular helper-like CD4+ T cells, intraepithelial lymphocytes, CD8+ and γδ T cell subsets, with skewed T cell antigen receptor repertoires. Mucosal changes remained detectable despite treatment, representing a persistent immune-epithelial 'scar'. Spatial transcriptomics defined transcriptional niches beyond those captured in conventional histological scores, including CD-specific lymphoid aggregates containing T cell-B cell interactions. Receptor-ligand spatial analyses integrated with disease susceptibility gene expression defined networks of altered chemokine and morphogen signaling, and provide potential therapeutic targets for CD prevention and treatment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: M.E.B.F. consults for Takeda Pharmaceuticals. N.M.P. has consulted for Infinitopes. D.R. is an employee of Janssen Immunology. D. Aschenbrenner is an employee of Novartis Institute of BioMedical Research. S.A.T. is a scientific advisory board member of ForeSite Labs, OMass Therapeutics, Qiagen and Xaira Therapeutics, a cofounder and equity holder of TransitionBio and Ensocell Therapeutics, a non-executive director of 10x Genomics, and a part-time employee of GlaxoSmithKline. J.A.T. consults for GSK, Vesalius, Avammune, Azenta, Dasman Diabetes Institute and Immunocore. P.K. has consulted for AZ, Infinitopes and UCB, and received research funding from Immunocore, all on unrelated projects. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












References
-
- Sollid, L. M. The roles of MHC class II genes and post-translational modification in celiac disease. Immunogenetics10.1007/s00251-017-0985-7 (2017). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

