The complete mitochondrial genome of Sinojackia microcarpa: evolutionary insights and gene transfer
- PMID: 40329166
- PMCID: PMC12054226
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11633-7
The complete mitochondrial genome of Sinojackia microcarpa: evolutionary insights and gene transfer
Abstract
Background: As a dicotyledonous plant within the Styracaceae family, Sinojackia microcarpa (S. microcarpa) is notable for its library-shaped fruit and sparse distribution, serving as a model system for studying the entire tree family. However, the scarcity of genomic data, particularly concerning the mitochondrial and nuclear sequences of S. microcarpa, has substantially impeded our understanding of its evolutionary traits and fundamental biological mechanisms.
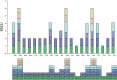
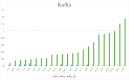
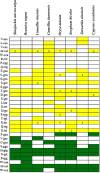
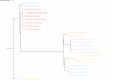
Results: This study presents the first complete mitochondrial genome sequence of S. microcarpa and conducts a comparative analysis of its protein-encoding genes across eight plant species. Our analysis revealed that the mitochondrial genome of S. microcarpa spans 687,378 base pairs and contains a total of 59 genes, which include 37 protein-coding genes (PCGs), 20 transfer RNA (tRNA) genes, and 2 ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes. Sixteen plastid-derived fragments strongly linked with mitochondrial genes, including one intact plastid-related gene (rps7), were identified. Additionally, Ka/Ks ratio analysis revealed that most mitochondrial genes are under purifying selection, with a few genes, such as nad9 and ccmB, showing signs of relaxed or adaptive evolution. An analysis of twenty-nine protein-coding genes from twenty-four plant species reveals that S. microcarpa exhibits a closer evolutionary relationship with species belonging to the genus Camellia. The findings of this study provide new genomic data that enhance our understanding of S. microcarpa, and reveal its mitochondrial genome's evolutionary proximity to other dicotyledonous species.
Conclusions: Overall, this research enhances our understanding of the evolutionary and comparative genomics of S. microcarpa and other plants in the Styracaceae family and lays the foundation for future genetic studies and evolutionary analyses in the Styracaceae family.
Keywords: Sinojackia microcarpa; Gene transfer; Mitochondria genome; Phylogenetic analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: We collected fresh leaf materials of Sinojackia microcarpa for this study. The plant samples and experimental research comply with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation. No specific permissions or licenses were required. Consent for publication: All co-authors have approved this study, and we affirm that the manuscript has not been published in any journal. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial genome assembly of the Chinese endemic species of Camellia luteoflora and revealing its repetitive sequence mediated recombination, codon preferences and MTPTs.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Apr 5;25(1):435. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06461-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40186100 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative mitochondrial genomics of Terniopsis yongtaiensis in Malpighiales: structural, sequential, and phylogenetic perspectives.BMC Genomics. 2024 Sep 12;25(1):853. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10765-6. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39267005 Free PMC article.
-
Complete mitochondrial genome sequence and comparative analysis of the cultivated yellow nutsedge.Plant Genome. 2022 Sep;15(3):e20239. doi: 10.1002/tpg2.20239. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Plant Genome. 2022. PMID: 35730918
-
Assembly and comparative analysis of the first complete mitochondrial genome of Setaria italica.Planta. 2024 Jun 8;260(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04386-2. Planta. 2024. PMID: 38850310
-
Complete mitochondrial genome assembly of Juglans regia unveiled its molecular characteristics, genome evolution, and phylogenetic implications.BMC Genomics. 2024 Sep 28;25(1):894. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10818-w. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39342114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shtolz N, Mishmar D. The mitochondrial Genome–on selective constraints and signatures at the organism, cell, and single mitochondrion levels. Front Ecol Evol 2019, 7.
-
- Kumar A, Choudhary A, Munshi A. Epigenetic reprogramming of MtDNA and its etiology in mitochondrial diseases. J Physiol Biochem 2024. - PubMed
-
- Chial H, Craig J. MtDNA and mitochondrial diseases. Nat Educ. 2008;1(1):217.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SRSJJD2024005/Off-campus practice education base for design majors of Zhejiang Shuren University
- SRSJJD2024005/Off-campus practice education base for design majors of Zhejiang Shuren University
- SRSJJD2024005/Off-campus practice education base for design majors of Zhejiang Shuren University
- SRSJJD2024005/Off-campus practice education base for design majors of Zhejiang Shuren University
- SXSZY202412/Key Specialty Project of Ordinary Colleges and Universities
- SXSZY202412/Key Specialty Project of Ordinary Colleges and Universities
- SXSZY202412/Key Specialty Project of Ordinary Colleges and Universities
- SXSZY202412/Key Specialty Project of Ordinary Colleges and Universities
- LGN21C160015/the Basic Public Welfare Research Projects of Zhejiang province
- LGN21C160015/the Basic Public Welfare Research Projects of Zhejiang province
- LGN21C160015/the Basic Public Welfare Research Projects of Zhejiang province
- LGN21C160015/the Basic Public Welfare Research Projects of Zhejiang province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

