The relationship between physical activity and social network site addiction among adolescents: the chain mediating role of anxiety and ego-depletion
- PMID: 40329384
- PMCID: PMC12057064
- DOI: 10.1186/s40359-025-02785-y
The relationship between physical activity and social network site addiction among adolescents: the chain mediating role of anxiety and ego-depletion
Abstract
Background and objectives: Physical activity is associated with social network site addiction in adolescents, yet the mechanisms remain unclear. This study examines whether anxiety and ego-depletion mediate this relationship.
Methods: A survey was conducted among 1,174 Chinese adolescents (614 boys, 560 girls; mean age = 12.59, SD = 1.13). Physical activity was assessed with a single item on moderate-to-vigorous exercise in the past 7 days. Social network site addiction, anxiety, and ego-depletion were measured using validated self-report questionnaires. Descriptive statistics, correlation analyses, and a chained mediation model were employed.
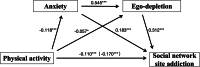
Results: Physical activity was negatively correlated with social network site addiction (r = -0.165, p < 0.001), anxiety (r = -0.121, p < 0.001), and ego-depletion (r = -0.119, p < 0.001). Anxiety was positively correlated with ego-depletion (r = 0.574, p < 0.001) and social network site addiction (r = 0.388, p < 0.001). Ego-depletion was positively associated with social network site addiction (r = 0.456, p < 0.001). Anxiety and ego-depletion sequentially mediated the relationship between physical activity and social network site addiction.
Conclusion: This study clarifies the psychological mechanisms linking physical activity and social network site addiction in adolescents, identifying anxiety and ego-depletion as key mediators. The findings emphasize the need to target these factors for more effective interventions.
Keywords: Adolescents; Anxiety; Ego-depletion; Physical activity; Social network site addiction.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Biomedicine Ethics Committee of Jishou University before the initiation of the project (Grant number: JSDX-2024-0086). And informed consent was obtained from the participants and their guardians before starting the program. We confirm that all the experiment is in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations such as the declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Global social media statistics research summary 2024 [May 2024]. 2024. p. Global social media research summary April 2024: The most recent and relevant statistics to help inform your social media marketing strategy.
-
- China Internet Network Information Center. (2024). The 53rd Statistical Report on the Development of the Internet in China.https://www.cnnic.cn/NMediaFile/2024/0325/MAIN1711355296414FIQ9XKZV63.pdf, 2024.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous