Analysis of the diagnostic and prognostic value of Peripheral blood mononuclear cell microRNA-9-5p in patients with sepsis in the intensive care unit
- PMID: 40330014
- PMCID: PMC12052792
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1509496
Analysis of the diagnostic and prognostic value of Peripheral blood mononuclear cell microRNA-9-5p in patients with sepsis in the intensive care unit
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-9-5p in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in sepsis patients.
Methods: Differentially expressed miR-9-5p in sepsis were screened from a database and available literature. Subsequently, iBMDM cell validation was conducted and the expression level of miR-9-5p in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was determined using RT-qPCR in 69 sepsis patients and 30 non-sepsis patients with infections, 24 hours after ICU admission. A control group that comprised 35 healthy individuals, matched for age and sex, was set up from those who agreed to provide blood samples laboratory analysis.
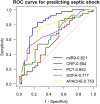
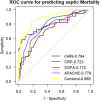
Results: On admission to the ICU, the levels of miR-9-5p were significantly higher in sepsis patients (10.13 [3.21, 24.94]) than in non-sepsis patients with infections (2.08 [1.68, 3.18]) and healthy controls (0.86 [0.36, 1.88]) (p < 0.001). The miR-9-5p levels were positively correlated with the severity of the disease as indicated by the SOFA score (r=0.656, P<0.001). The AUC of miR-9-5p in predicting sepsis, septic shock, and in-hospital death was 0.825, 0.821, and 0.845, respectively.
Conclusion: Elevated expression levels of miR-9-5p in peripheral blood mononuclear cells are significantly associated with an increased risk of sepsis and septic shock, and also indicate a higher risk of organ dysfunction.
Keywords: diagnosis; microRNA-9-5p; peripheral blood mononuclear cell; prognosis prediction; sepsis.
Copyright © 2025 Ye, Wang, Ji, Li, Liang, Liu, Cao and Shao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
[Value of serum miR-155-5p and miR-133a-3p expression for the diagnosis and prognosis evaluation of sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016 Aug;28(8):694-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2016.08.005. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016. PMID: 27434558 Chinese.
-
Serum miR-181a-5p Serves as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Sepsis and Predicts Clinical Outcomes.APMIS. 2025 Jun;133(6):e70037. doi: 10.1111/apm.70037. APMIS. 2025. PMID: 40550759
-
miRNA sequencing identifies immune-associated miRNAs and highlights the role of miR-193b-5p in sepsis and septic shock progression.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 13;15(1):5323. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89946-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39948173 Free PMC article.
-
Four serum microRNAs identified as diagnostic biomarkers of sepsis.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012 Oct;73(4):850-4. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e31825a7560. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012. PMID: 23026916
-
[The value of coagulation indicators combined with sequential organ failure assessment in assessing disease severity and prognosis of elderly patients with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Nov;36(11):1133-1139. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240424-00374. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39697016 Chinese.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

