Cryo-EM reveals conformational variability in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD induced by two broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies
- PMID: 40330036
- PMCID: PMC12053377
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra00373c
Cryo-EM reveals conformational variability in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD induced by two broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies
Abstract
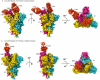
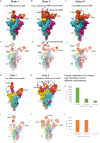
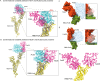
SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins play a critical role in infection by interacting with the ACE2 receptors. Their receptor-binding domains and N-terminal domains exhibit remarkable flexibility and can adopt various conformations that facilitate receptor engagement. Previous structural studies have reported the RBD of the spike protein in "up", "down", and various intermediate states, as well as its different conformational changes during ACE2 binding. This flexibility also influences its interactions with the neutralizing antibodies, yet its role in the antibody complexes remains understudied. In this study, we used cryo-electron microscopy to investigate the structural properties of two broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, THSC20.HVTR04 and THSC20.HVTR26. These antibodies were isolated from an unvaccinated individual and demonstrated potent neutralization of multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants. Our analysis revealed distinct binding characteristics and conformational changes in the spike RBD upon binding with the monoclonal antibodies. The structural characterization of the spike protein-monoclonal antibody complexes provided valuable insights into the structural variability of the spike protein and the possible mechanisms for antibody-mediated neutralization.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
A patent application (PCT/IB2022/057923) was filed on the invention of novel monoclonal antibodies with the following inventors: Jayanta Bhattacharya, Nitin Hingankar, Payel Das, Suprit Deshpande, Pallavi Kshetrapal, Ramachandran Thiruvengadam, Amit Awasthi, Zaigham Abbas Rizvi. Authors Randhir Singh and Sowrabha Jayatheertha are employed by Mynvax Private Limited, Basavanagudi, Bengaluru 560004, India, and author Poorvi M. Reddy was employed by Mynvax Private Limited, Basavanagudi, Bengaluru 560004, India. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lan J. Ge J. Yu J. Shan S. Zhou H. Fan S. Zhang Q. Shi X. Wang Q. Zhang L. Wang X. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature. 2020;581:215–220. - PubMed
-
- Yajima H. Anraku Y. Kaku Y. Kimura K. T. Plianchaisuk A. Okumura K. Nakada-Nakura Y. Atarashi Y. Hemmi T. Kuroda D. Takahashi Y. Kita S. Sasaki J. Sumita H. Ito J. Maenaka K. Sato K. Hashiguchi T. Structural basis for receptor-binding domain mobility of the spike in SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 and JN.1. Nat. Commun. 2024;15:8574. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

