Identification of ageing-associated gene signatures in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction by integrated bioinformatics analysis and machine learning
- PMID: 40330147
- PMCID: PMC12053710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101478
Identification of ageing-associated gene signatures in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction by integrated bioinformatics analysis and machine learning
Abstract
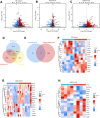
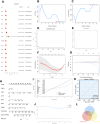
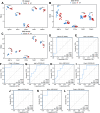
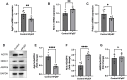
The incidence of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) increases with the ageing of populations. This study aimed to explore ageing-associated gene signatures in HFpEF to develop new diagnostic biomarkers and provide new insights into the underlying mechanisms of HFpEF. Mice were subjected to a high-fat diet combined with L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester (l-NAME) to induce HFpEF, and next-generation sequencing was performed with HFpEF hearts. Additionally, separate datasets were acquired from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were used to identify ageing-related DEGs. Support vector machine, random forest, and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator algorithms were employed to identify potential diagnostic genes from ageing-related DEGs. The diagnostic value was assessed using a nomogram and receiver operating characteristic curve. The gene and related protein expression were verified by reverse transcription PCR and western blotting. The immune cell infiltration in hearts was analysed using the single-sample gene-set enrichment analysis algorithm. The results showed that the merged HFpEF datasets comprised 103 genes, of which 15 ageing-related DEGs were further screened in. The ageing-related DEGs were primarily associated with immune and metabolism regulation. AGTR1a, NR3C1, and PRKAB1 were selected for nomogram construction and machine learning-based diagnostic value, displaying strong diagnostic potential. Additionally, ageing scores were established based on nine key DEGs, revealing noteworthy differences in immune cell infiltration across HFpEF subtypes. In summary, those results highlight the significance of immune dysfunction in HFpEF. Furthermore, ageing-related DEGs might serve as promising prognostic and predictive biomarkers for HFpEF.
Keywords: Ageing; Bioinformatics analysis; HFpEF; Immune dysfunction; Machine learning.
© 2024 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltdé.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic potential of energy metabolism-related genes in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 27;14:1296547. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1296547. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38089628 Free PMC article.
-
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: new insights from bioinformatics.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Feb;10(1):416-431. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14211. Epub 2022 Oct 20. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 36266995 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying of immune-associated genes for assessing the obesity-associated risk to the offspring in maternal obesity: A bioinformatics and machine learning.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Mar;30(3):e14700. doi: 10.1111/cns.14700. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38544384 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Epicardial Adipose Tissue-Derived Proteins in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Atrial Fibrillation: A Bioinformatics Analysis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Sep 6;17:6093-6111. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S466203. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39257896 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptomic analysis and machine learning for characterizing diagnostic biomarkers and immune cell infiltration in fetal growth restriction.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 4;15:1381795. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1381795. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39295860 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nonlinear association between visceral fat metabolism score and heart failure: insights from LightGBM modeling and SHAP-Driven feature interpretation in NHANES.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s12911-025-03076-7. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2025. PMID: 40597284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dunlay S.M., Roger V.L., Redfield M.M. Epidemiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017;14(10):591–602. - PubMed
-
- Guo J., Petersen M.R., Tang H., Meece L.E., Shao H., Ahmed M.M. Cost effectiveness of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors compared with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists among patients with heart failure and a reduced ejection fraction. Cardiovasc Innov Appl. 2023;8(1) doi: 10.15212/CVIA.2023.0037. - DOI
-
- Deng Y., Xie M., Li Q., et al. Targeting mitochondria-inflammation circuit by β-hydroxybutyrate mitigates HFpEF. Circ Res. 2021;128(2):232–245. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

