Influencing Factors of Diabetic Patients of on Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 40330188
- PMCID: PMC12051797
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v54i3.18240
Influencing Factors of Diabetic Patients of on Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: A Scoping Review
Abstract
Background: The oral health-related quality of life in diabetic patients is regarded as a significant factor for assessing their dental health. This study aimed to examine the current research state, frequently utilized research instruments, and factors impacting the oral health quality of life in individuals with diabetes.
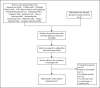
Methods: Our review was conducted according to the PRISMA extended guidelines for scoping review. We conducted a literature review on the oral health and quality of life of diabetic patients using PubMed, Embase, and additional databases. This research proposal has been formally submitted to the Open Science Framework.
Results: Out of 3827 materials, merely 17 publications satisfied the review requirements for our study. The search period extended from the inception of the library until Feb 5, 2024. The research encompassed seven countries, including China, the United States, and Iran, utilizing the Oral Health Evaluation Index for the Elderly and the Oral Health Impact Scale as prevalent assessment instruments. The quality of life connected to oral health was predominantly low among diabetic patients, influenced by socio-demographic characteristics, oral health status, biochemical indicators, psychosocial elements, lifestyle choices, and oral-related factors.
Conclusion: The oral health-related quality of life among diabetic patients is typically diminished. Oral health care professionals must devise strategies to promptly identify, assess, and manage the factors influencing the oral health-related quality of life in diabetic patients, while incorporating necessary preventive measures and screenings to enhance oral disease prevention in routine evaluations.
Keywords: Determinants; Diabetes; Evaluation instrument; Oral health-related quality of life; Scoping review.
Copyright© 2025 Xian et al Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
References
-
- Hills AP, Arena R, Khunti K, et al. (2018). Epidemiology and determinants of type 2 diabetes in south Asia. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 6(12):966–78. - PubMed
-
- Goldney J, Barker MM, Thomas M, et al. (2024). Age at onset of type 2 diabetes and prevalence of vascular disease and heart failure: Systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. J Diabetes Complications, 38(10):108849. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources