Efficacy of a Neuroimmune Therapy Including Pineal Methoxyindoles, Angiotensin 1-7, and Endocannabinoids in Cancer, Autoimmune, and Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 40330271
- PMCID: PMC12050209
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S513910
Efficacy of a Neuroimmune Therapy Including Pineal Methoxyindoles, Angiotensin 1-7, and Endocannabinoids in Cancer, Autoimmune, and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
Purpose: Recent advancements in psycho-neuro-endocrine-immunology indicate that numerous noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) originate from disruptions in the cytokine immune network, resulting in chronic inflammatory responses. This persistent low-degree inflammation is attributed to deficiencies in crucial endogenous anti-inflammatory neuroendocrine systems, including the pineal gland, the endocannabinoid system, and the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 / angiotensin 1-7 axis. The administration of pineal methoxyindoles (melatonin, 5-methoxytryptamine), cannabinoids, and angiotensin 1-7 may entail potential therapeutic benefits for NCDs, particularly for patients who do not respond to conventional treatments.
Patients and methods: This study evaluates the safety and efficacy of a neuroimmune regimen comprising melatonin (100 mg/day at night), 5-methoxytryptamine (30 mg in the early afternoon), angiotensin 1-7 (0.5 mg twice daily), and cannabidiol (20 mg twice daily) in 306 patients with NCDs, including advanced cancer, autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, depression, and cardiovascular disease.
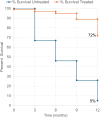
Results: The neuroimmune regimen successfully halted cancer progression in 68% of cancer patients, who also reported improvements in mood, sleep, and relief from anxiety, pain, and fatigue. In patients with autoimmune diseases, the treatment effectively controlled the disease process, remarkable in cases of multiple sclerosis. Additionally, positive outcomes were observed in patients with Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and depression.
Conclusion: Randomized controlled trials are required to assess this therapeutic approach for NCDs that includes endogenous neuroendocrine molecules regulating immune responses in an anti-inflammatory manner.
Keywords: 5-methoxytryptamine; melatonin; metainflammation; noncommunicable diseases; oxytocin; pinoline.
© 2025 Lissoni et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang Y, Xie Y, Zhang C, et al. The systemic immune inflammation index as a novel predictive biomarker for contrast-induced acute kidney injury risk following percutaneous coronary intervention: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2024;23. doi:10.2174/0115701611328810241028112700 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

