A Reticulated Rash With Rapid Recovery
- PMID: 40330356
- PMCID: PMC12054334
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81788
A Reticulated Rash With Rapid Recovery
Abstract
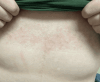
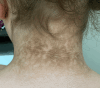
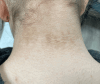
Confluent and Reticulated Papillomatosis (CARP) is a rare and benign dermatosis, however, it can cause immense cosmetic insecurities in affected patients. It is most common on the trunk and neck, more common in female patients than male patients, and there appears to be a correlation with overweight and obese body mass index levels. Many of the patients presenting with CARP are adolescents who are especially vulnerable to resultant social isolation and embarrassment due to the cosmetic insecurities they face from CARP. For this reason, prompt diagnosis and treatment of the condition is critical. There are many conditions that can mimic CARP, with acanthosis nigricans being the most common, however, CARP has a much more direct and timely treatment option. We present a case of a 13-year-old female patient with a complaint of a three-year history of stable discoloration to the chest and neck who was able to achieve clearance in just eight weeks with the appropriate treatment.
Keywords: acanthosis nigricans; carp; confluent and reticulated papillomatosis; hyperpigmented reticular rash; reticulated rash.
Copyright © 2025, Simon et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Confluent and Reticulated Papillomatosis Resembling Pityriasis Versicolor and Acanthosis Nigricans: Case Report.JMIR Dermatol. 2023 Mar 2;6:e41245. doi: 10.2196/41245. JMIR Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37632912 Free PMC article.
-
Resolution of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis after bariatric surgery.Clin Obes. 2021 Feb;11(1):e12427. doi: 10.1111/cob.12427. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Clin Obes. 2021. PMID: 33164331
-
Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis : a review of the literature.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006;7(5):305-13. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200607050-00004. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006. PMID: 17007541 Review.
-
Differentiating confluent and reticulated papillomatosis from acanthosis nigricans.J Cutan Pathol. 2015 Dec;42(12):944-952. doi: 10.1111/cup.12581. Epub 2015 Sep 28. J Cutan Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26264983
-
Concomitant confluent and reticulated papillomatosis and acanthosis nigricans in an obese girl with insulin resistance successfully treated with oral minocycline: Case report and published work review.J Dermatol. 2017 Aug;44(8):954-958. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.13819. Epub 2017 Mar 11. J Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28295566 Review.
References
-
- Retrospective review of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis in pediatric patients. Xiao TL, Duan GY, Stein SL. Pediatr Dermatol. 2021;38:1202–1209. - PubMed
-
- Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: clinical, light and electron microscopic studies. Jimbow M, Talpash O, Jimbow K. Int J Dermatol. 1992;31:480–483. - PubMed
-
- Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a review of the literature. Scheinfeld N. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2006;7:305–313. - PubMed
-
- Focal hypohidrosis in lesional skin in a probable case of confluent and reticulated papillomatosis: a case report with insight into the pathomechanism of recurrence. Shimoda-Komatsu Y, Mizukawa Y, Yamazaki Y, Ohyama M. J Dermatol. 2023;50:266–270. - PubMed
-
- Differentiating confluent and reticulated papillomatosis from acanthosis nigricans. Park YJ, Kang HY, Lee ES, Kim YC. J Cutan Pathol. 2015;42:944–952. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
