Targeting angiogenesis in gastrointestinal tumors: strategies from vascular disruption to vascular normalization and promotion strategies angiogenesis strategies in GI tumor therapy
- PMID: 40330478
- PMCID: PMC12052729
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1550752
Targeting angiogenesis in gastrointestinal tumors: strategies from vascular disruption to vascular normalization and promotion strategies angiogenesis strategies in GI tumor therapy
Abstract
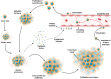
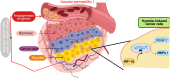
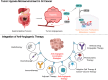
Angiogenesis plays a critical role in the progression of gastrointestinal (GI) tumors, making it an important therapeutic target. This review explores recent advancements in targeting angiogenesis for GI tumor therapy, highlighting strategies that range from vascular disruption to vascular promotion. The biological foundation of tumor angiogenesis is discussed, with a focus on the molecular mechanisms that regulate this process, including key players such as VEGF, HIFs, and non-coding RNAs. Current therapeutic strategies, including anti-angiogenic agents, vascular normalization approaches, and emerging vascular promotion therapies, are analyzed for their clinical applications and limitations. Additionally, the review examines combination strategies that integrate anti-angiogenic therapy with chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and other modalities to enhance efficacy and overcome resistance. Despite significant progress, challenges such as drug resistance, tumor heterogeneity, and adverse effects remain. Future research directions emphasize the discovery of novel molecular targets, development of personalized treatments, and innovative combination therapies to optimize outcomes for patients with GI tumors. This comprehensive review provides a foundation for advancing angiogenesis-targeted therapies in GI cancer treatment.
Keywords: angiogenesis; clinical applications; gastrointestinal tumors; molecular mechanisms; therapeutic strategies; vessel disruption.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Li and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trends and Challenges in Tumor Anti-Angiogenic Therapies.Cells. 2019 Sep 18;8(9):1102. doi: 10.3390/cells8091102. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31540455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting VEGF signaling for tumor microenvironment remodeling and metastasis inhibition: Therapeutic strategies and insights.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 May;186:118023. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118023. Epub 2025 Mar 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40164047 Review.
-
The role of VEGF in Cancer angiogenesis and tumorigenesis: Insights for anti-VEGF therapy.Cytokine. 2025 May;189:156908. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2025.156908. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Cytokine. 2025. PMID: 40049050 Review.
-
Clinical significance of angiogenesis in gastrointestinal cancers: a target for novel prognostic and therapeutic approaches.Ann Surg. 2003 Jul;238(1):9-28. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000075047.47175.35. Ann Surg. 2003. PMID: 12832961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-angiogenic therapy, a new player in the field of sarcoma treatment.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014 Aug;91(2):172-85. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Feb 15. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24613529 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

